Thick-billed flowerpecker facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Thick-billed flowerpecker |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| D. a. modestum from Kaeng Krachan, Phetchaburi, Thailand |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Dicaeidae |
| Genus: | Dicaeum |
| Species: |
D. agile
|
| Binomial name | |
| Dicaeum agile (Tickell, 1833)
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Piprisoma squalidum |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
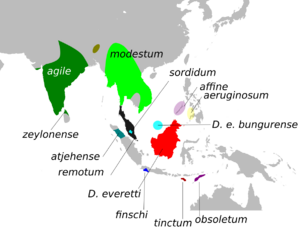
The thick-billed flowerpecker (Dicaeum agile) is a very small bird. It belongs to a group of birds called flowerpeckers. These birds mostly eat fruits. They are very active and often seen high up in the trees in forests. This bird lives in many parts of tropical southern Asia, from India all the way to Indonesia and Timor. There are different groups of these birds, called subspecies, living in different areas. Some of these groups are even thought to be their own separate species.
Contents
What Does the Thick-billed Flowerpecker Look Like?
This flowerpecker is about 10 centimeters (4 inches) long. It has a dark, strong beak and a short tail. Its back is dark grey-brown. Its belly is a dull grey with light streaks on a pale yellow-brown color. The lower back feathers are a bit more olive green. Its eyes are reddish.
It is hard to tell the difference between male and female birds just by looking at them. Young birds have a lighter color at the base of their beak. They also have fewer streaks on their underside. The tips of their tail feathers have small white spots.
Different groups of these birds live in different places. For example, the group found in India is called the "nominate race." The group in Sri Lanka is smaller and darker. Other groups live in places like Burma, Sumatra, Java, and the Philippines. Some of these groups are now considered completely separate species.
How Do Thick-billed Flowerpeckers Live?
Like other flowerpeckers, these birds mainly eat berries and nectar. Sometimes, they also eat insects. Many of these birds live in thick forests. However, the group in India often lives in gardens or open forests.
The thick-billed flowerpecker eats mistletoe berries differently from some other flowerpeckers. Instead of swallowing the seeds, it wipes them off on a tree branch. It then eats only the fruit part. This helps spread the mistletoe plant to nearby branches. In Sri Lanka, these birds usually look for food higher up in the trees.
When they are looking for food, these birds often make a "spick" sound. They also jerk their tail from side to side when they are sitting on a branch. When a male bird wants to attract a female, he will sing a rambling song. He also flutters around her. His song sounds a bit like another bird, the ashy prinia. During this display, the male can raise the feathers on his head. This makes the white bases of these feathers show, looking like a white stripe on his head.
Nesting and Reproduction
The nest of the thick-billed flowerpecker looks like a dry leaf. This helps to hide it. It is shaped like a hanging purse. The birds build it using spiderwebs and thin plant fibers. They hang it from a thin branch, usually 3 to 15 meters (10 to 50 feet) high. They are known to often build their nests near the nests of Oecophylla smaragdina ants.
In southern India, the breeding season is from December to March. Both the male and female birds help build the nest. A female usually lays about 3 eggs, but sometimes it can be 2 or 4. The eggs hatch after about 13 days. The young birds are ready to leave the nest after about 18 days.
Gallery
-
Thick-billed Flowerpecker Dicaeum agile on Helicteres isora in Narsapur, India.
-
Illustration of nest by Joseph Wolf
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |




