Transcription factor facts for kids
Transcription factors are special proteins that help control when and how genes work in our bodies. Think of them as switches that turn genes on or off, or make them work faster or slower.
Each transcription factor knows exactly where to go on your DNA. It finds and sticks to a specific part of the DNA sequence. By doing this, it helps control how much genetic information is copied from DNA into something called messenger RNA (mRNA). This copying process is called transcription.
Sometimes, transcription factors are called 'DNA-binding factors' because they stick to DNA. They can work alone or with other proteins to either help or stop an enzyme called RNA polymerase. RNA polymerase is super important because it's the one that copies the genetic instructions from DNA to mRNA for specific genes.
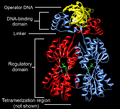
Transcription factors have special parts called DNA-binding domains (DBDs). These DBDs are like tiny hands that grab onto the DNA right next to the genes they need to control. Other proteins also help with gene control, but they aren't called transcription factors because they don't have these DNA-binding parts.
Contents
What are Transcription Factors?
Transcription factors are proteins that play a key role in how your body uses its genetic information. They act like managers for your genes, making sure the right genes are active at the right time.
How do they work?
Transcription factors control the process of transcription. This is the first step in gene expression, where the instructions in a gene are copied from DNA into a messenger molecule called mRNA. This mRNA then carries the instructions to make proteins.
- Turning genes on (Upregulation): Some transcription factors help RNA polymerase attach to the DNA, which speeds up the copying process and makes more mRNA. This is like turning a light switch on or making it brighter.
- Turning genes off (Downregulation): Other transcription factors can block RNA polymerase, slowing down or stopping the copying process. This is like turning a light switch off or dimming it.
Why are they important?
Controlling genes is vital for everything your body does. It helps cells grow, develop, and respond to changes around them. For example, transcription factors make sure that muscle cells only make muscle proteins, and brain cells only make brain proteins.
Glossary of Key Terms
Here are some important words to help you understand more about transcription factors:
- gene expression – This is the whole process where the information from a gene is used to create something useful, like a protein.
- transcription – The first step of gene expression, where a copy of a gene is made from DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA) by RNA polymerase.
- transcription factor – A protein that sticks to DNA and helps control how genes are used by either helping or stopping transcription.
- transcriptional regulation – This means controlling how fast genes are copied into mRNA.
- upregulation or activation – When transcription factors increase the speed at which a gene is copied.
- downregulation or repression – When transcription factors decrease the speed at which a gene is copied.
- coactivator – A protein that works with transcription factors to increase gene copying.
- corepressor – A protein that works with transcription factors to decrease gene copying.
- response element – A specific part of the DNA where a transcription factor attaches.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Factor de transcripción para niños
In Spanish: Factor de transcripción para niños