Treaty of Sugauli facts for kids

Bhimsen Thapa's Gorkha troops (right) at Segauli, (c. 1849)
|
|
| Drafted | 2 December 1815 |
|---|---|
| Signed | 4 March 1816 |
| Location | Sugauli, India |
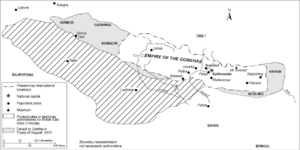
| Condition | one fourth of Nepalese controlled territory was ceded to British East India Company |
| Expiration | None |
| Signatories |
|
| Parties | |
| Language | English |
The Treaty of Sugauli was an important agreement signed on March 4, 1816. It set the borders for Nepal and ended a war between Nepal and the East India Company. This company was a powerful British trading group that controlled much of India at the time. The treaty was signed by Guru Gajaraj Mishra for Nepal and Parish Bradshaw for the East India Company.
Contents
Why the Treaty Was Needed
After Nepal became a bigger country under Prithvi Narayan Shah, it started expanding its land. This led to conflicts with the British, who controlled nearby parts of India. A series of battles, known as the Anglo-Nepalese War, happened between 1814 and 1816.
In 1815, a British general named David Ochterlony pushed the Nepalese army out of the Garhwal and Kumaon regions. These areas are now part of Uttarakhand, India. The Nepalese had controlled these lands for about 12 years, and their rule was quite strict.
General Ochterlony offered peace to Nepal. He wanted the British to have some influence over Nepal and for Nepal's borders to be set, similar to how they are today. Nepal first said no to these terms. This led to more fighting the next year, with British forces moving closer to the Kathmandu Valley. Because of this, Nepal finally agreed to the treaty.
What the Treaty Said
The treaty was first drafted in December 1815 in Sagauli, Bihar. It asked Nepal to give up all the lands it had taken to the west and east of its current borders. Nepal also had to give up a large flat area called the Tarai.
A very important part of the treaty was that Nepal had to accept a permanent British representative, or 'resident,' in Kathmandu. This person would live in Nepal's capital. The Nepalese government was not happy with these terms at first. However, they agreed to sign the treaty in March 1816. This happened after General Ochterloney's army moved very close to Kathmandu, only about 30 miles away.
Nepal's Location and Trade
Nepal has a long history of trading salt with Tibet. This trade route was very important for the economy of the Kathmandu valley. The East India Company had made a lot of money from trade routes in India. So, they were interested in controlling Nepal's trade routes too.
Nepal was a relatively new country at the time, and its borders were not always clear or well-guarded. Because of this, and their desire for trade routes, the British East India Company declared war on Nepal. This was the Anglo-Nepalese War, which lasted from 1814 to 1816.
Nepal had a strong army, known as the Gurkhas. These soldiers were also of interest to the British company. But Nepal was a smaller country. Eventually, it had to agree to a ceasefire under the terms of the Sugauli Treaty.
Why Nepal Signed the Treaty
The British East India Company had three main goals. They wanted to use Nepal's impressive army, have a British official watch over the Nepali court, and use Nepal's trade routes to Tibet.
Naturally, the Nepali court was not fully happy about signing the treaty. It caused a lot of debate. Bhimsen Thapa, who was Nepal's prime minister at the time, understood something important. He realized that the best way to keep Nepal free from outside control was to give the British what they mainly wanted: a safe and peaceful border. So, to protect Nepal's independence and safety, the treaty was signed.
From the British side, it seemed easier to control certain aspects of Nepal through a treaty than to try and fully take over the country.
What Happened After the Treaty
The treaty brought about 30 years of peace. However, new problems started to appear around 1840. For example, in June 1840, there was a mutiny (a rebellion) in the Nepali army. Soldiers were upset about possible pay cuts. They were led to believe that the British had forced these cuts on the Nepali government. This almost led to an attack on the British resident's home.
Another worrying event happened in 1842. This was during a debt lawsuit involving an Indian merchant named Kasinath Mull. The British resident in Nepal, Brian Hodgson, seemed very forceful. This made people in the Nepali court suspect that the British were trying to control their decisions. These events show that the treaty's goal of preventing tensions might still be debated.
The Boundary Treaty of 1860
In 1857, a big rebellion started in India against British rule. It is sometimes called the First War of Independence. During this time, a group of Gurkha soldiers from Nepal helped the British. Their support helped the British succeed. This created a friendlier relationship between Nepal and Britain.
Because of this improved relationship, the Sugauli Treaty was changed in Nepal's favor. This new agreement was called the Boundary Treaty of 1860. It gave Nepal more independence and returned some land to it.
Current Border Issues
Even today, there are some disagreements about the India–Nepal border. The most important disputes are in the Susta and Kalapani regions. These two areas cover about 40 kilometers of the border between India and Nepal.
See also
- Nepal–Britain Treaty of 1860
- 1950 Indo-Nepal Treaty of Peace and Friendship
- Gurkha War
- Kingdom of Nepal
- Naya Muluk - land in western Terai restored to Nepal in 1860
- Prithvi Narayan Shah
- Sikkim
- Unification of Nepal