Turtleheart facts for kids
Turtleheart (also known as Turtle's Heart) was an important leader and warrior of the Delaware people, also called the Lenape. His name in the Unami language was Tahkoxitèh. He lived during a time of big conflicts, including the French and Indian Wars and Pontiac's War. Turtleheart, along with another Lenape chief named Killbuck, represented the Delaware Nation at a major meeting called the Treaty of Fort Stanwix in 1768.
Early Life
We don't know exactly when Turtleheart was born or when he passed away. Some people believe he might have been the brother of Chief Custaloga from the Wolf Clan. He might also have been the father or uncle of a famous leader known as Captain Pipe. In 1763, Turtleheart lived in an Indian village called Shaningo. This village was located near a smaller river that flowed into Big Beaver Creek.
Pontiac's War
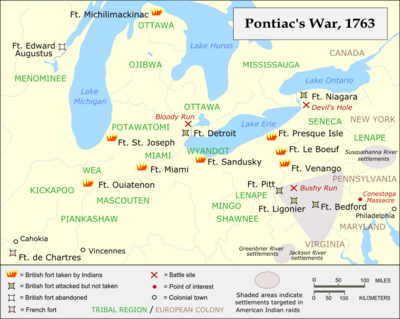
Pontiac's War began in May 1763. It was a big uprising by many Native American tribes against the British. The tribes were upset because the British had taken over lands that used to belong to the French. A powerful leader named Pontiac brought many tribes together. They planned to attack all the British forts and trading posts.
One of the goals was to remove British traders from the area. A captive named John McCullough saw some traders being attacked. He wrote that many traders were killed, and their goods were taken. Some traders tried to escape to Fort Pitt.
On May 27, 1763, Turtleheart visited a trading post near Fort Pitt. He seemed worried and in a hurry. He bought a lot of gunpowder and lead. Turtleheart also warned a trader named Alexander McKee to leave the area quickly. He told McKee that if he didn't leave soon, he might not see him alive again. This showed that Turtleheart knew the attacks were about to begin.
Reports to Colonel Henry Bouquet stated that Turtleheart was involved in the killing of traders John Calhoon and Thomas Coplin near Beaver Creek.
Siege of Fort Pitt
The Siege of Fort Pitt began on June 22, 1763. A siege is when an army surrounds a fort or city to try and capture it. The Native American warriors attacked Fort Pitt, but it was too strong to be taken easily. So, they kept the fort surrounded throughout July.
On June 24, Turtleheart and another chief named Mamaltee approached the fort. They spoke with a British officer. They told the British that other forts, like Ligonier, had been destroyed. They warned that many Native American warriors were coming. Turtleheart and Mamaltee suggested that the British leave the fort and go back to their own country.
The British commander, Simeon Ecuyer, thanked them but refused to leave. He said the fort had everything it needed and could defend itself. He also said that three large British armies were coming to fight the Native Americans.
Smallpox Incident
During this meeting, something unusual happened. The British commander, Simeon Ecuyer, gave two blankets and a handkerchief to Turtleheart and Mamaltee. These items had been taken from the smallpox hospital. Smallpox was a very dangerous disease at that time. The British hoped that these "tainted gifts" would spread the illness among the Native American tribes.
This idea was discussed between Colonel Henry Bouquet and his superior, Sir Jeffrey Amherst. Amherst wrote that they should "send the small pox among the disaffected tribes of Indians." Bouquet agreed and said he would try to "inocculate the Indians by means of Blankets."
Later, the British general Thomas Gage approved the payment for these items. A severe smallpox outbreak did affect Native American tribes in the Ohio Valley in 1763 and 1764. Historians believe this attempt to spread the disease was effective and impacted the war.
Treaty of Fort Stanwix
In 1768, Turtleheart and Chief Killbuck represented the Delaware Nation at the Treaty of Fort Stanwix. This was a very important meeting. It was led by Sir William Johnson. The purpose of the treaty was to set up a clear boundary line between the lands of the British colonies and the Native American tribes. This was done following orders from King George I.
Many Native American leaders attended the treaty. By October 22, 1768, about 2,200 Native Americans had gathered at Fort Stanwix. More chiefs arrived the next day, and the main discussions began on October 24.
Turtleheart signed the treaty, showing his agreement. However, he did not make a speech or a formal presentation during the treaty discussions.