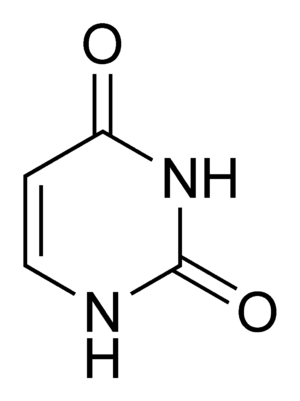
Uracil facts for kids
Uracil is a special chemical building block. It is a type of base found inside RNA, which is like a messenger molecule in your body's cells. Uracil is very similar to another base called thymine, which is found in DNA. In fact, uracil takes the place of thymine in RNA.
Uracil was first discovered in 1900. It belongs to a group of chemicals called pyrimidines.
Contents
What is Uracil?
Uracil is one of the four main bases that make up RNA. Think of RNA as a set of instructions that helps your body build proteins. These instructions are written using a special code made from these bases.
- Uracil is often written with the letter "U".
- It is a small molecule with a ring shape.
- Scientists first found uracil over 120 years ago.
How Does Uracil Work in RNA?
In RNA, uracil has a very important job. It helps to carry genetic information. When RNA is being made from DNA, uracil steps in where thymine would normally be.
- Uracil always connects with another base called adenine.
- This connection is called a "base pair."
- These pairs help RNA molecules form their correct shapes.
Uracil vs. Thymine: What's the Difference?
Uracil and thymine are very similar, but they have one small difference. This difference is key to why they are found in different molecules.
- Thymine is found in DNA, which stores your genetic information long-term.
- Uracil is found in RNA, which carries short-term messages.
- This small change helps cells tell DNA and RNA apart.
Why is Uracil Important?
Uracil is essential for all living things. Without it, our cells could not make RNA properly. This would stop our bodies from making the proteins they need to grow and function.
- It helps carry genetic instructions from DNA to the parts of the cell that make proteins.
- Uracil plays a role in how genes are expressed.
- It is a basic part of the genetic code of life.
See also
 In Spanish: Uracilo para niños
In Spanish: Uracilo para niños
 | Percy Lavon Julian |
 | Katherine Johnson |
 | George Washington Carver |
 | Annie Easley |