Vedic period facts for kids
The Vedic period was a time in the history of the Indian subcontinent. It lasted from about 1500 BC to 600 BC. This period came after the end of the Indus Valley Civilization.
The name "Vedic" comes from the Vedas. These are ancient religious texts. They tell us a lot about how people lived during this time. The Vedas are our main source of information for this period.
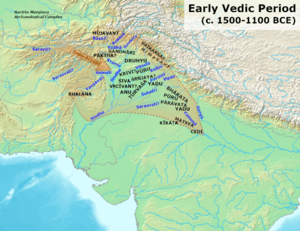
The Vedas were created and passed down by people who spoke an old Indo-Aryan language. These people moved into the northwestern parts of India early in this period. At first, the Vedic culture was based on tribes and raising animals. This was true until about 1200 or 1100 BC. The main area for this culture was the Punjab region.
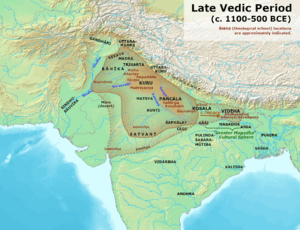
Later, the society moved eastward into the Ganges Plain. People started to farm more and settled down in one place. During the Vedic period, different social classes began to appear. Small kingdoms, called Janapadas, also started to form. We can see signs of Vedic culture in different archaeological finds. These include the Ochre Coloured Pottery culture and the Painted Grey Ware culture.
Images for kids
-
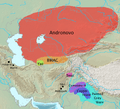
Archaeological cultures linked to Indo-Iranian migrations. The Andronovo and BMAC cultures are often connected to Indo-Iranian movements. The Gandhara grave, Cemetery H, Copper Hoard, and Painted Grey Ware cultures might be linked to Indo-Aryan movements.
-
A modern copy of tools and a falcon-shaped altar. These were used for the Agnicayana ritual. This important ritual started in the Kuru Kingdom around 1000 BCE.
-
A ceramic goblet from Navdatoli, Malwa, from 1300 BCE.
-
An early 19th-century handwritten copy of the Rigveda. It is written in the Devanagari script. The special Vedic sounds are marked in red.
See also
 In Spanish: Periodo védico para niños
In Spanish: Periodo védico para niños
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |