Indo-Aryan peoples facts for kids
|
|
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| ~1.5 billion | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| over 911 million | |
| over 190 million | |
| over 160 million | |
| over 26 million | |
| over 14 million | |
| over 2 million | |
| over 725,400 | |
| over 300,000 | |
| over 240,000 | |
| Languages | |
| Indo-Aryan languages | |
| Religion | |
| Indian religions (Mostly Hindu; with Buddhist, Sikh and Jain minorities) and Islam, Christians and some non-religious atheist/agnostic | |
The Indo-Aryan peoples are a group of people who speak Indo-Aryan languages. They live mostly in the Indian subcontinent, which includes countries like India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives.
Historically, the early Indo-Aryans were herders who spoke Indo-Iranian languages. They moved from Central Asia into South Asia. This movement is known as the Indo-Aryan migrations. They brought with them the early form of the Proto-Indo-Aryan language.
These early Indo-Aryan groups were closely related. They belonged to the same larger Indo-Iranian family. They lived north of the Indus River. This connection is clear in their shared culture, language, and history.
Contents
History of Indo-Aryan Peoples
Early Migrations
The Indo-Aryan languages arrived in the Indian subcontinent because of a migration. This movement of Indo-Aryan peoples came from Central Asia. They moved into the northern Indian subcontinent. This area includes modern-day Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
These migrations began around 1800 BCE. They happened after the invention of the war chariot. These movements also brought Indo-Aryan languages to other places. This included the Levant (a region in the Middle East) and possibly Inner Asia.
Another group of Indo-Aryans moved west. They created the Mitanni kingdom in northern Syria. This was around 1500–1300 BC. Another important group was the Vedic people. Some historians suggest that the Wusun, an ancient group in Inner Asia, might also have been of Indo-Aryan origin.
Origins and Culture
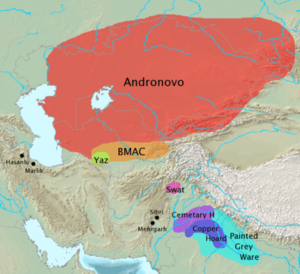
The ancestors of the Indo-Aryans are called the Proto-Indo-Iranians. They are linked to the Sintashta culture (2100–1800 BCE). They are also connected to the Andronovo culture. This culture thrived from about 1800–1400 BCE. It was found in the steppes around the Aral Sea. This area is now Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan.
The Proto-Indo-Aryans separated from the Iranians around 1800–1600 BCE. They moved south through the Bactria-Margiana Culture (BMAC). This was south of the Andronovo culture. They adopted some unique religious ideas from the BMAC. Then, they moved further south into the Levant and northwestern India.
The migration of the Indo-Aryans was part of a larger spread. This was the spread of Indo-European languages. These languages came from the Proto-Indo-European homeland. This homeland was in the Pontic–Caspian steppe. This larger movement started in the 4th millennium BCE.
Several ancient cultures are thought to be linked to the Indo-Aryans. These include the Gandhara Grave Culture, Cemetery H, Copper Hoard Culture, Ochre Coloured Pottery Culture, and Painted Grey Ware Culture.
The Indo-Aryans were connected by shared cultural norms and language. They used the word aryā, which means 'noble'. Over thousands of years, Indo-Aryan culture has changed a lot. Especially in India, it has mixed with the cultures of local people. This blending created the unique Indo-Aryan culture we see today.
This culture and language spread through a system where powerful groups supported others. This allowed different groups to join and adopt this culture. This explains why it had such a strong influence on other cultures it met.
Genetic Background
Genetically, most Indo-Aryan-speaking people today are a mix. They have ancestors from Central Asian steppe herders. They also have ancestors from Iranian hunter-gatherers. To a smaller degree, they have ancestors from South Asian hunter-gatherers. These South Asian hunter-gatherers are also known as Ancient Ancestral South Indians (AASI).
Dravidian-speaking people are also a mix. They have ancestors from South Asian hunter-gatherers and Iranian hunter-gatherers. They have fewer ancestors from Central Asian steppe herders. Tribal Dravidian groups in South India mostly come from South Asian hunter-gatherers. They have fewer Iranian hunter-gatherer ancestors.
Also, people who speak Austroasiatic and Tibeto-Burmese languages have added to the genetic makeup of South Asia.
Some ideas, like Indigenous Aryanism, suggest that Indo-Aryans started in India. They claim that Indo-European languages then spread from India to Central Asia and Europe. However, modern research and scientific data do not support this idea. It is mainly based on certain beliefs, not on facts.
Historical Indo-Aryan Groups
Here are some groups of people who were part of the historical Indo-Aryan peoples:
- Anga
- Bahlikas
- Bharatas
- Caidyas
- Dewa
- Gāndhārīs
- Gangaridai
- Gurjara-Pratihara
- Gupta
- Kambojas
- Kalinga
- Kasmira
- Kekaya
- Khasas
- Kikata
- Koliya
- Kosala
- Kurus
- Licchavis
- Madra
- Magadhis
- Malavas
- Mallakas
- Mātsyeyas
- Moriya
- Nishadhas
- Odra
- Pakthas
- Pala
- Panchala
- Paundra
- Puru
- Salva
- Salwa
- Saraswata
- Sauvira
- Shakya
- Shunga
- Sindhu
- Sudra
- Surasena
- Trigarta
- Utkala
- Vanga
- Vatsa
- Vidarbha
- Videha
- Yadava
- Yadu
Modern Indo-Aryan Groups
Many different groups today are considered Indo-Aryan peoples. They are often named after the languages they speak or the regions they live in.
- Assamese people
- Awadhi people
- Banjara people
- Bengali people
- Bhil people
- Bhojpuri people
- Bishnupriya Manipuri people
- Brokpa people
- Chakma people
- Deccani people
- Dhivehi people
- Dogra people
- Garhwali people
- Gujarati people
- Halba people
- Haryanvi people
- Jaunsari people
- Kalash people
- Kashmiri people
- Khas people
- Kho people
- Kohistani people
- Konkani people
- Kumauni people
- Kutchi people
- Magahi people
- Muhajir people
- Maithil people
- Marathi people
- Marwari people
- Nagpuria people
- Odia people
- Palula people
- Pashayi people
- Pahari people
- Punjabi people
- Rajasthani people
- Romani people
- Rohingya people
- Sadan people
- Saraiki people
- Saurashtra people
- Shina people
- Sindhi people
- Sinhalese people
- Thari people
- Tharu people
- Thori people
- Tirahi people
- Torwali people
- Warli people
See also
- Proto-Indo-Europeans
- Indo-Iranians
- Dardic peoples
- Aryan
- Indo-Aryan languages
- Indo-Aryan migrations
- Indigenous Aryanism
- Aryan race
- Aryavarta
- Dasa
- Dravidian peoples
- Early Indians
- South Asian diaspora
- Northern South Asia
 | William Lucy |
 | Charles Hayes |
 | Cleveland Robinson |

