Pala Empire facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Pala Empire
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8th century–12th century | |||||||||||
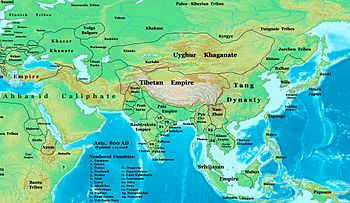
The Pala Empire in Asia in 800 CE
|
|||||||||||
| Capital |
List
Bikrampur
Pataliputra Gauda Monghyr (Devapala) Somapura (Dharampala) Mahipal in present-day Murshidabad district (Mahipala I) Ramavati in Varendra (Ramapala and successors) |
||||||||||
| Common languages | Sanskrit, Prakrit (including proto-Bengali) | ||||||||||
| Religion | Mahayana Buddhism, Tantric Buddhism, Shaivism | ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||
|
• 8th century
|
Gopala | ||||||||||
|
• 12th century
|
Madanapala | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Classical India | ||||||||||
|
• Established
|
8th century | ||||||||||
|
• Disestablished
|
12th century | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Today part of | Bangladesh India Nepal Pakistan |
||||||||||
The Pala Empire was a powerful kingdom in ancient India. It ruled over parts of northern and eastern India, especially the areas known today as Bengal and Bihar. This empire lasted for about 400 years, from the 8th to the 12th century. The word Pala (Modern Bengali: পাল pal) means "protector". All the kings of this empire had "Pala" at the end of their names.
Contents
Founding and Growth of the Pala Empire
How the Pala Empire Began
The Pala Empire was founded by a king named Gopala. He became king in 750 CE. What was special about Gopala's rise to power is that he was chosen by an election. This was very unusual for that time! Gopala ruled for 20 years, from 750 to 770 CE. He made sure the Palas controlled all of Bengal.
Expanding the Empire's Power
After Gopala, two other important kings took over. They were Dharmapala (who ruled from 770-810 CE) and Devapala (who ruled from 810-850 CE). These kings made the empire much bigger. They expanded Pala control across a large part of the northern and eastern Indian subcontinent.
End of the Pala Empire
The Pala Empire eventually became weaker. It finally ended in the 12th century. This happened after attacks from another powerful group called the Sena dynasty.
Culture and Religion of the Palas
Buddhism and Art
The Pala kings were strong followers of Buddhism. They especially followed the Mahayana and Tantric types of Buddhism. They built many beautiful temples and created amazing works of art. Their art often showed Buddhist figures and stories.
Learning and Universities
The Palas were also big supporters of education. They helped famous universities like Nalanda and Vikramashila. These universities were important centers of learning in ancient India. Many students and scholars came there to study.
Spreading Buddhism to Tibet
The Pala Empire played a very important role in spreading Buddhism. They helped establish Buddhism in Tibet. Buddhist teachers from the Pala Empire traveled to Tibet and shared their knowledge. This helped shape the religion in Tibet.
Images for kids
-
Nalanda is considered one of the first great universities in recorded history. It reached its height under the Palas.
-
Atisha was a Buddhist teacher, who helped establish the Sarma lineages of Tibetan Buddhism.
-
Somapura Mahavihara, a World Heritage Site, was built by Dharmapala
See also
 In Spanish: Dinastía Pala para niños
In Spanish: Dinastía Pala para niños













