Integer facts for kids
Integers are special numbers in mathematics. They are like the natural numbers (1, 2, 3, ...) and their opposites (like -1, -2, -3, ...). Zero is also an integer. Think of integers as "whole" numbers. They don't have any fractions or decimals. For example, 17 is an integer, but 17.5 is not.
Contents
What Are Integers?
Integers are numbers that can be positive, negative, or zero.
- Positive integers are numbers like 1, 2, 3, and so on.
- Negative integers are numbers like -1, -2, -3, and so on.
- Zero (0) is an integer, but it is neither positive nor negative.
An integer is a rational number that doesn't have any "part" or "fraction." This means there are no numbers after the decimal separator other than zeros. For example, the integer 5 is the same as the decimal 5.0 or 5.00.
Integers on a Number Line
You can see integers clearly on a number line. The number line shows numbers stretching out forever in both directions. 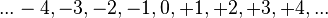 On a number line:
On a number line:
- Numbers to the right of zero are positive.
- Numbers to the left of zero are negative.
- The further a number is to the right, the larger it is.
- The further a number is to the left, the smaller it is.
No Smallest or Largest Integer
Integers go on forever in both directions. There is no smallest integer because you can always find a smaller negative number (like -100 is smaller than -50). There is also no largest integer because you can always find a larger positive number (like 1000 is larger than 500). Each integer has a number right before it and a number right after it. For example, after 3 comes 4, and before 3 comes 2. Consecutive integers are integers that follow each other in order, like 3, 4, 5, 6.
Doing Math with Integers
When you do math with integers, the results are often also integers.
Adding and Subtracting Integers
- When you add two integers, the answer is always an integer.
* Example: 5 + 3 = 8 (8 is an integer) * Example: -2 + 7 = 5 (5 is an integer) * Example: -4 + (-1) = -5 (-5 is an integer)
- When you find the difference (subtract) between two integers, the answer is always an integer.
* Example: 10 - 4 = 6 (6 is an integer) * Example: 2 - 8 = -6 (-6 is an integer) * Example: -5 - (-3) = -2 (-2 is an integer)
Multiplying Integers
- When you multiply two integers, the answer is always an integer.
* Example: 6 × 2 = 12 (12 is an integer) * Example: -3 × 4 = -12 (-12 is an integer) * Example: -5 × -2 = 10 (10 is an integer) * Even complex calculations like (12 + 2345 × (67 - 8)) × 9 will result in an integer if all numbers involved are integers.
Dividing Integers
- When you divide one integer by another, the answer is sometimes not an integer.
* Example: 10 / 2 = 5 (5 is an integer) * Example: 123 / 45 = 2.733... (This is not an integer because it has a decimal part.)
Integers in Programming
In computer programming, integers are very important. Many programming languages have a special type of data called "int" or "integer." This data type is used to store whole numbers. For example, in a language like C, if you want to count how many times something happens, you would use an "int" variable. This helps computers work efficiently with whole numbers without needing to deal with decimals.
See also
 In Spanish: Número entero para niños
In Spanish: Número entero para niños

