Western rosewood facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Western rosewood |
|
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Acacia
|
| Species: |
spania
|
 |
|
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
The Western rosewood (scientific name: Acacia spania) is a special type of tree. It belongs to the Acacia family, which is known for its many different kinds of trees and shrubs. This tree is found only in a specific part of northeastern Australia, meaning it's endemic there.
About the Western Rosewood
The Western rosewood is a tree that usually has one main trunk. It can grow quite tall, reaching about 15 meters (50 feet) high. Its bark looks a bit like iron.
Its branches are light brown and have a slightly rough, scaly feel. They are also glabrous, which means they are smooth and hairless.
Leaves and Flowers
Like many Acacia trees, the Western rosewood doesn't have typical leaves. Instead, it has phyllodes. These are flattened leaf stems that look and act like leaves.
The phyllodes of the Western rosewood are smooth and stay green all year round. They are shaped like a narrow oval, from flat to slightly curved. Each phyllode is about 2 to 4.5 centimeters (0.8 to 1.8 inches) long and 6 to 18 millimeters (0.2 to 0.7 inches) wide. They are usually grey-green to blue-green and feel quite stiff. You can see three to five main lines, or nerves, running along them.
The tree blooms between August and September. Its flowers grow in cylinder-shaped spikes that are 2 to 5 centimeters (0.8 to 2 inches) long. The flowers themselves are bright yellow to lemon yellow.
Where It Grows
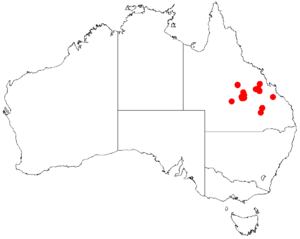
The Western rosewood is found in a small area along the central coast of Queensland, Australia. You can mostly find it near Emerald.
It often grows in red soils, sometimes forming thick groups of trees in woodland areas. It often shares its home with different kinds of Eucalyptus trees and other Acacia species.
This tree usually grows on rocky sandstone ridges and hills. It prefers sandy to loamy soils. You can find it at altitudes between 400 to 600 meters (1,300 to 2,000 feet) above sea level. Its natural range covers an area of about 205,000 square kilometers (79,000 square miles), stretching from north of Aramac down to Roma in the south.

