Acetylcholine facts for kids
Acetylcholine (say: ah-set-ul-KOH-leen) is a super important chemical in your body. Think of it like a tiny messenger! It helps your nerves talk to each other and to your muscles. This amazing chemical helps you do everything from thinking and remembering to moving your arms and legs. It's produced in your brain and helps carry information from your senses, like touch and smell.
Contents
What is Acetylcholine?
Acetylcholine is a special kind of chemical called a neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitters are like tiny mail carriers that send signals between nerve cells, also known as neurons. These signals are how your brain and body communicate. Acetylcholine was one of the very first neurotransmitters ever discovered!
How Does Acetylcholine Work?
Imagine your body is a giant network of wires. Acetylcholine is the electricity that flows through some of these wires.
- When a nerve cell wants to send a message, it releases acetylcholine into a tiny gap called a synaptic cleft.
- On the other side of the gap, another cell (like a muscle cell or another nerve cell) has special "receivers" called receptors.
- Acetylcholine locks into these receptors, like a key fitting into a lock.
- This "unlocks" the receptor, causing the second cell to react. This reaction could be a muscle contracting or another nerve signal starting.
What Does Acetylcholine Do?
Acetylcholine plays many important roles in your body, helping with both voluntary and involuntary actions.
Muscle Movement
One of its most famous jobs is helping your muscles move.
- When you decide to kick a ball or wave your hand, your brain sends a signal down your nerves.
- At the end of these nerves, acetylcholine is released.
- This chemical tells your muscles to contract, allowing you to move. Without enough acetylcholine, your muscles wouldn't get the message to move!
Brain Functions
Acetylcholine is also very active in your brain, especially in areas linked to:
- Learning: It helps your brain form new memories and understand new information.
- Memory: It plays a big part in remembering things, from what you had for breakfast to facts for a test.
- Attention: It helps you focus and pay attention to what's happening around you.
- Sleep: It's involved in regulating your sleep cycles, especially during the dream stage (REM sleep).
Other Body Functions
This busy chemical also helps control parts of your body you don't even think about, like:
- Your heart rate
- How much you sweat
- How your digestive system works
Where is Acetylcholine Found?
Acetylcholine is found throughout your nervous system.
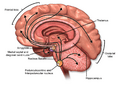
- It's in your brain, produced in specific areas like the nucleus basalis (a small but mighty part of your brain).
- It's also in your spinal cord and in the nerves that go out to your muscles and organs.
Images for kids
-
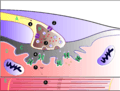
Muscles contract when they receive signals from motor neurons. The neuromuscular junction is the site of the signal exchange. The steps of this process in vertebrates occur as follows: (1) The action potential reaches the axon terminal. (2) Calcium ions flow into the axon terminal. (3) Acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft. (4) Acetylcholine binds to postsynaptic receptors. (5) This binding causes ion channels to open and allows sodium ions to flow into the muscle cell. (6) The flow of sodium ions across the membrane into the muscle cell generates an action potential which induces muscle contraction. Labels: A: Motor neuron axon B: Axon terminal C: Synaptic cleft D: Muscle cell E: Part of a Myofibril
-
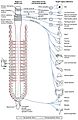
Components and connections of the parasympathetic nervous system.
-
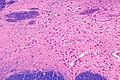
Micrograph of the nucleus basalis (of Meynert), which produces acetylcholine in the CNS. LFB-HE stain.
See also
 In Spanish: Acetilcolina para niños
In Spanish: Acetilcolina para niños