Adenosine triphosphate facts for kids
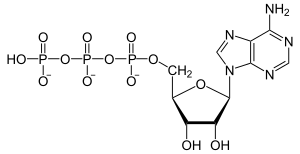
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is like the energy currency of your body's cells. It's a special molecule called a nucleotide that helps cells do their work. Think of it as tiny energy packets that move chemical energy around inside your cells to power everything they do, like growing, moving, and thinking!
Every single cell in your body needs ATP for energy. It's made up of a part called adenine and three phosphate groups. When your body needs to make ATP, it uses a special helper called ATP synthase to combine a simpler molecule called adenosine diphosphate (ADP, which has two phosphate groups) with another phosphate.
Contents
How ATP Works
ATP is super useful! It can be used for many different things. The energy it holds is stored right in its chemical bonds.
When ADP (which has two phosphates) connects with another phosphate, energy is stored. This is like charging a battery! This process is called an endothermic reaction because it takes in energy.
When ATP breaks off one of its phosphate groups and becomes ADP, energy is set free. This is like using the energy from a battery! This process is called an exothermic reaction because it releases energy.
The way ATP and ADP swap phosphate groups is a never-ending cycle. It only stops when a cell dies.
What ATP Does in Cells
ATP is the main energy source for most of what cells do. This includes building big molecules like DNA and RNA, and making proteins. ATP also helps move large molecules across cell membranes, like when cells take things in (called endocytosis) or push things out (called exocytosis).
Making DNA and RNA
In all living things, the building blocks for DNA are made from RNA building blocks. Special enzymes called ribonucleotide reductases (RNR) change the sugar part of RNA into the sugar part needed for DNA.
When cells make RNA, ATP is one of the four main building blocks that get added directly into the RNA molecule. The energy to connect these blocks comes from breaking off two phosphate groups from ATP. Making DNA is similar, but first, ATP is changed into a special DNA building block before it's added.
History of ATP
- ATP was found in 1929 by Karl Lohmann and Jendrassik. Around the same time, Cyrus Fiske and Yellapragada Subba Rao also discovered it.
- In 1941, Fritz Albert Lipmann suggested that ATP acts as the go-between for energy-making and energy-using reactions in cells.
- The first time ATP was made in a lab was in 1948 by Alexander Todd.
- In 1997, Paul D. Boyer and John E. Walker shared half of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. They figured out how ATP is made by enzymes. Jens C. Skou received the other half for finding an enzyme that moves ions, called Na+, K+ -ATPase.
Images for kids
-
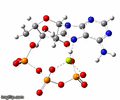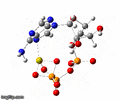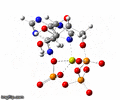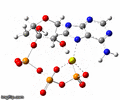
This image shows a spinning view of a magnesium-ATP molecule.
See also
 In Spanish: Adenosín trifosfato para niños
In Spanish: Adenosín trifosfato para niños