Nucleotide facts for kids
A nucleotide is a very important tiny molecule. Think of nucleotides as the basic building blocks for two super important molecules in all living things: RNA and DNA. These two molecules, RNA and DNA, carry all the instructions that make you, well, YOU! They are found in every living creature on Earth.
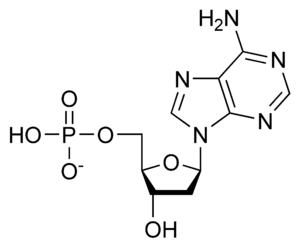
Each nucleotide is made of three main parts. First, there's a nucleobase, which is also called a nitrogenous base. Second, there's a five-carbon sugar. This sugar can be either ribose or deoxyribose. Third, there's at least one phosphate group. The nitrogenous bases come in two main types: purines or pyrimidines.
Contents
Parts of a Nucleotide
A nucleotide is like a small LEGO brick with three distinct pieces.
The Sugar Part
The sugar in a nucleotide is a special five-carbon sugar. If the sugar is ribose, the nucleotide is called a ribonucleotide. These are the building blocks of RNA. If the sugar is deoxyribose, the nucleotide is called a deoxyribonucleotide. These are the building blocks of DNA.
The Base Part
The nitrogenous base is the part that carries the "code." In DNA, there are four different bases:
In RNA, the bases are similar, but uracil (U) takes the place of thymine. So, RNA has:
- Adenine (A)
- Guanine (G)
- Cytosine (C)
- Uracil (U)
These bases pair up in a very specific way. In DNA, adenine always connects with thymine. Guanine always connects with cytosine. These pairs are held together by special bonds called hydrogen bonds. This pairing is super important for how DNA works!
The Phosphate Part
The phosphate group is like the "connector" piece. It links one nucleotide to the next, forming long chains that make up DNA and RNA.
Nucleotides and Your Body's Energy
Nucleotides do more than just build DNA and RNA. They also play a huge role in how your body gets and uses energy.
Energy for Cells
Think of nucleotides as tiny batteries for your cells. They provide the chemical energy needed for many important cell jobs. For example, they help your body:
- Make amino acids and proteins.
- Build and repair cell membranes.
- Move cells and parts inside cells.
- Help cells divide and grow.
Cell Signaling and Helpers
Nucleotides also help cells "talk" to each other. This is called cell signaling. They are also important cofactors. Cofactors are like helpful assistants that make enzymes (special proteins that speed up reactions) work better. Some examples of these helpers are coenzyme A and FAD.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Nucleótido para niños
In Spanish: Nucleótido para niños
 | May Edward Chinn |
 | Rebecca Cole |
 | Alexa Canady |
 | Dorothy Lavinia Brown |