Alligator juniper facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Alligator juniper |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Cupressaceae |
| Genus: | Juniperus |
| Species: |
J. deppeana
|
| Binomial name | |
| Juniperus deppeana Steud.
|
|
 |
|
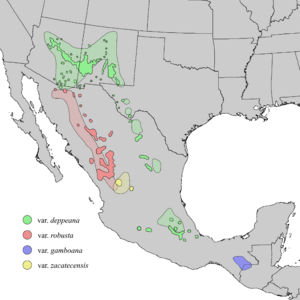
| Natural range of Juniperus deppeana | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Alligator Juniper is a cool tree! It's also known as the checkerbark juniper. Its scientific name is Juniperus deppeana. Some Native American names for it include táscate and tláscal. These trees are usually small to medium-sized. They grow about 10 to 15 meters (33 to 49 feet) tall. Some can even reach 25 meters (82 feet)!
You can find Alligator Junipers in central and northern Mexico. They also grow in the southwestern United States. This includes Arizona, New Mexico, and western Texas. They like to grow on dry ground. You'll find them at medium heights, from about 750 to 2700 meters (2,460 to 8,860 feet) up.
Contents
What Makes Alligator Junipers Special?
Its Unique Bark
The Alligator Juniper gets its name from its bark. The bark is usually very special. It looks different from other juniper trees. It is hard and dark gray-brown. The bark cracks into small square plates. These plates look a lot like alligator skin! Sometimes, though, the bark can be stringy. This is more like other junipers.
Leaves and Cones
The small branches of the tree are about 1 to 1.5 millimeters thick. The leaves are arranged in pairs or groups of three. Adult leaves are tiny and scale-like. They are 1 to 2.5 millimeters long. On the main shoots, they can be up to 5 millimeters long. Young seedlings have needle-like leaves. These are longer, about 5 to 10 millimeters.
The cones of the Alligator Juniper look like berries. They are 7 to 15 millimeters wide. They start green and turn orange-brown when they are ripe. They also have a whitish, waxy coating. Each cone holds 2 to 6 seeds. It takes about 18 months for the cones to ripen. Birds and mammals love to eat these cones. The male cones are smaller, about 4 to 6 millimeters long. They release their pollen in the spring.
Most Alligator Junipers are dioecious. This means each tree usually has cones of only one sex. So, one tree will have only male cones, and another will have only female cones. But sometimes, a tree can be monoecious. This means it has both male and female cones on the same tree.
Different Types of Alligator Juniper
Scientists have found five different types, or varieties, of Alligator Juniper. Not all experts agree that they are all truly separate types. These varieties can be found in different parts of the tree's range. They might have small differences in their leaves or the size of their cones. For example, some have dull gray-green leaves. Others have a white spot on each leaf. Some varieties also have larger cones.
Uses of the Alligator Juniper
The berry-like cones of the Alligator Juniper are an important food source. Many birds and mammals eat them.
See also
 In Spanish: Juniperus deppeana para niños
In Spanish: Juniperus deppeana para niños
 | Chris Smalls |
 | Fred Hampton |
 | Ralph Abernathy |




