Blue-tailed hummingbird facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Blue-tailed hummingbird |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Saucerottia cyanura | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Saucerottia
|
| Species: |
cyanura
|
 |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Amazilia cyanura |
|
The blue-tailed hummingbird is a small, colorful bird known for its bright blue tail. It's a type of hummingbird that lives in parts of Central America, including Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, and Nicaragua. These amazing birds are part of a group often called "emeralds" because of their shiny green feathers.
Contents
About the Blue-tailed Hummingbird
What's in a Name?
Scientists often group animals together based on how they are related. The blue-tailed hummingbird used to be in a group called Amazilia. But in 2014, new studies looked closely at their DNA. These studies showed that the Amazilia group wasn't quite right.
So, most scientists decided to move the blue-tailed hummingbird to a different group. This new group is called Saucerottia. It's like moving from one family branch to another that fits better!
Different Types of Blue-tailed Hummingbirds
There are three main types, or subspecies, of the blue-tailed hummingbird. They are:
- S. c. cyanura (the main type)
- S. c. guatemalae
- S. c. impatiens
Each of these types has slight differences, like where they live or how dark their feathers are.
Appearance and Features
The blue-tailed hummingbird is a small bird. It is about 9 to 10 centimeters (around 3.5 to 4 inches) long. A male bird might weigh about 3.9 grams, which is less than a nickel! Females are a bit heavier, weighing around 4.5 grams.
Colors of the Male Hummingbird
Male blue-tailed hummingbirds are very striking. They have a black beak with a reddish bottom part. Their head and back are a deep, shiny metallic green. Their lower back feathers are a dull purplish-bronze. The feathers covering their tail are a dark metallic blue.
When their wings are closed, you can see a patch of chestnut color. Their tail is a beautiful dark metallic violet-blue. Most of their belly is a bright metallic green. The feathers under their tail are a dull steel blue.
Colors of the Female Hummingbird
Female blue-tailed hummingbirds look similar to males but are not as bright. Their lower back is less purplish. The green feathers on their belly often have thin white edges. They might also have some dull whitish-buff feathers on their belly. The feathers under their tail are grayish.
Subspecies Differences
- S. c. guatemalae : This type is much darker than the main type. Its wing feathers are a darker chestnut. Its tail can be more violet or metallic purple. The feathers under its tail are dark steel blue or even blue-black.
- S. c. impatiens : This type is a bit bigger than the main type. Its head and back are a darker green. The reddish-brown patch on its wings is larger. The feathers under its tail are dull steel blue with rich reddish-brown edges.
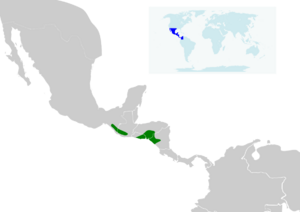
Where They Live
The blue-tailed hummingbird lives in several countries in Central America.
- The S. c. guatemalae type is found along the Pacific coast, from southern Mexico to southern Guatemala.
- The main type, S. c. cyanura, lives in southern Honduras, eastern El Salvador, and northwestern Nicaragua.
- The S. c. impatiens type is found in northwestern and central Costa Rica.
Their Favorite Places
These hummingbirds like to live in many different kinds of places. They prefer semi-open areas, such as:
- Edges of humid and dry oak and pine forests
- Forest clearings
- New forests that are growing back (secondary forests)
- Areas with bushes and shrubs (scrublands)
- Coffee farms where coffee plants grow under shade trees
You can find them at different heights above sea level. In Mexico and Guatemala, they live between 100 and 1,800 meters (about 330 to 5,900 feet) high. In El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua, they live from near sea level up to 1,200 meters (about 3,900 feet) high.
How They Behave
Moving Around
Scientists don't know much about whether blue-tailed hummingbirds migrate or move around a lot. Their movements haven't been studied in detail yet.
What They Eat
Blue-tailed hummingbirds mostly eat nectar from flowers. They can find nectar at all levels of their habitat, from low bushes to tall trees. They are known to visit Inga trees for food. Like other hummingbirds, they probably also eat small insects. Insects provide them with important protein.
Raising a Family
Not much is known about how blue-tailed hummingbirds raise their young. Scientists haven't found or described their nests or eggs yet. This means there's still a lot to learn about their breeding habits!
Sounds They Make
The song of the blue-tailed hummingbird is described as a "short twitter." They also make different calls. These include a "hard, raspy bzzzrt" sound, sharp "chips," and a high, sharp "siik!" sound they make while flying.
Conservation Status
The IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) has evaluated the blue-tailed hummingbird. They have listed it as a species of "Least Concern." This means that it is not currently considered to be in danger of disappearing.
The bird has a large area where it lives. Scientists estimate there are at least 50,000 adult blue-tailed hummingbirds. However, this number is thought to be slowly decreasing. Even so, no immediate major threats have been found. Human activities probably don't have a big short-term effect on these hummingbirds.


