Antonio Maria Valsalva facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Antonio Maria Valsalva
|
|
|---|---|

Antonio Maria Valsalva
|
|
| Born | 17 January 1666 Imola
|
| Died | 2 February 1723 (aged 57) |
| Nationality | Italian |
| Known for | Valsalva maneuver |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Anatomist |
| Academic advisors | Marcello Malpighi |
| Notable students | Giovanni Battista Morgagni |
Antonio Maria Valsalva (born January 17, 1666 – died February 2, 1723) was an Italian anatomist from Imola. He spent a lot of time studying the anatomy of the ears. He is known for naming the Eustachian tube and describing parts of the heart called the aortic sinuses of Valsalva.
His name is also connected to the Valsalva maneuver. This is a special breathing technique used to test how well your circulatory system works. Other body parts named after him include Valsalva’s muscle and taeniae Valsalvae. He also discovered that if one side of your body is weak because of a brain injury, the injury is usually on the opposite side of the brain. This idea is called the "Valsalva doctrine."
Contents
About Antonio Maria Valsalva
Valsalva was born in a town called Imola. He first went to a Jesuit school where he learned about subjects like history, math, and natural sciences. After that, he studied medicine and philosophy at the University of Bologna.
There, he learned from a famous scientist named Marcello Malpighi. Malpighi was one of the first people to study tiny parts of the body using a microscope. Valsalva finished medical school in 1687.
In 1695, he became a surgeon at the Hospital of the Incurables in Bologna. Later, in 1705, he became a professor of anatomy at the University of Bologna. He also became the president of a science and arts institute.
One of Valsalva's most famous students was Giovanni Battista Morgagni. Morgagni later put together all of Valsalva's writings and wrote a book about his life in 1740.
Valsalva married Elena Lisi in 1709. He passed away in Bologna in 1723. He was buried in a church in Bologna.
Valsalva's family gave a collection of dried body parts to the Institute of Sciences. These were used to help students learn about the human body. This collection later inspired artists to create wax models of the heart and lungs. These models are now in the Museum of Anatomy.
People described Valsalva as a very skilled surgeon and an excellent physician. He was also known as a careful anatomist who was very honest in his science. He was also a very kind person. Morgagni once wrote that "nobody of those times goes ahead of him, very few who are his equals."
Valsalva's Important Discoveries
Valsalva studied and taught many subjects. These included science, surgery, anatomy, physiology (how the body works), and even psychiatry (mental health). When he was young, he successfully removed a dog's kidney.
He believed in treating wounds without burning them, which was common back then. He also thought that people with mental illnesses should be treated kindly. His main focus was on the middle and inner parts of the ear. This included the muscles around the ear and in the throat.
Valsalva was the one who named the Eustachian tube. He also explained how it works and what its muscle does. He showed how the mastoid cells (small air spaces behind the ear) are connected to the tympanic cavity (the middle ear). He also studied how the ear works normally and when it has problems.
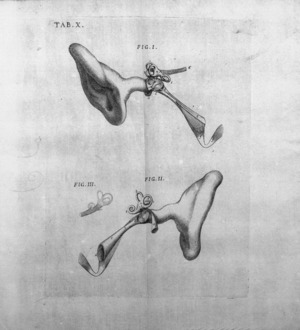
In 1704, he published a book called De aure humana tractatus (Treatise on the Human Ear). This book describes the Valsalva maneuver. This maneuver is a way to test if your auditory tubes (Eustachian tubes) are open.
Valsalva's Published Works
- De aure humana tractatus (Treatise on the Human Ear), published in 1735. This book describes the complete structure of the ear. It includes many new discoveries and pictures. It also looks into how all the parts of the ear work. The book also has a new description and drawing of the muscles of the uvula and pharynx.
Valsalva Device in Spacesuits
The Valsalva device is a special tool used in spacesuits. It helps astronauts equalize the pressure in their ears. They can do the Valsalva maneuver inside their suit without using their hands to pinch their nose. This device can also be used for other things, like removing moisture from an astronaut's face.