Arithmetic logic unit facts for kids
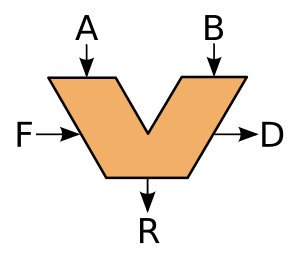
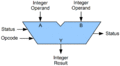
An arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a special part inside a computer's central processing unit (CPU). Think of it as the brain's calculator and decision-maker. It's a digital circuit that does all the basic math problems, like adding and subtracting, and also makes logical decisions, like checking if one number is bigger than another.
Every computer, even the smallest ones like those in a microwave or a toy robot (called microcontrollers), has an ALU. It's a super important part of how computers work!
Contents
What an ALU Does
The ALU performs two main types of operations:
Arithmetic Operations
These are the math calculations you know. The ALU can:
- Add numbers (like 2 + 3)
- Subtract numbers (like 5 - 1)
- Multiply numbers
- Divide numbers
It does these calculations incredibly fast, many times a second!
Logic Operations
Besides math, the ALU also makes logical decisions. These are like "yes" or "no" questions. For example, it can:
- Check if two numbers are equal
- See if one number is greater than another
- Figure out if a number is positive or negative
These simple decisions help the computer follow instructions and run programs.
Where ALUs are Found
The ALU is a core part of the CPU, which is like the main brain of your computer, tablet, or smartphone.
In Modern Computers
Today's computers have very powerful and complex ALUs. Some advanced CPUs even have more than one ALU! This allows them to do many calculations at the same time, making them super fast. For example, a superscalar CPU might have several ALUs working together to speed things up.
History of the ALU
The idea for the ALU was first suggested in 1945 by a famous mathematician named John von Neumann. He helped design some of the earliest computers, and his ideas are still used in computers today.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Unidad aritmética lógica para niños
In Spanish: Unidad aritmética lógica para niños