Aspergillus flavus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Aspergillus flavus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
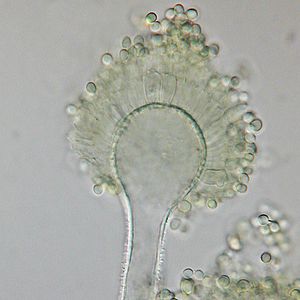
| A conidiophore of A. flavus | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order: | Eurotiales |
| Family: | Trichocomaceae |
| Genus: | Aspergillus |
| Species: |
A. flavus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aspergillus flavus Link (1809)
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Aspergillus flavus is a type of fungus that can be quite dangerous. It's found all over the world, especially in soil. This fungus often grows on cereal grains, beans, and tree nuts.
Besides infecting crops before and after they are harvested, many types of A. flavus make harmful chemicals called mycotoxins. If these chemicals are eaten, they can be poisonous to mammals, including humans. The specific toxin made by A. flavus is called 'aflotoxin'.
A. flavus can cause diseases in both humans and animals. For mammals, eating food with aflatoxins can lead to liver cancer. It can also cause a serious infection called aspergillosis in people whose immune systems are not working well.
Contents
Why is A. flavus dangerous?
In 1960, something very serious happened on a farm in England. About 100,000 turkeys died! Scientists discovered the cause was the turkeys' main food, peanut meal, which was infected with A. flavus. When the fungus was studied, four toxic chemicals, later named aflatoxins, were found.
Tests on the dead turkeys showed that these aflatoxins severely damaged their livers, either killing liver cells or causing tumors. This event led to new, stricter rules for how food for people is produced, which also made food production more expensive.
Protecting our food crops
To keep grains and legumes safe from A. flavus infection, farmers need to take certain steps. These steps are important before, during, and after the harvest.
- Moisture levels: Food should be kept very dry, with moisture levels below 11.5%.
- Temperature: Storage areas should be kept as cool as possible. A. flavus cannot grow below 5°C (41°F). Low temperatures also help keep the food fresh and reduce moisture.
- Pest control: Using fumigation helps get rid of insects and mites. These tiny pests can help spread the fungus.
- Cleanliness: Removing old, unripe, damaged, or broken seeds, and keeping storage areas clean, also helps stop the fungus from spreading.
Natural ways to fight A. flavus
Scientists are looking for natural ways to stop A. flavus from harming crops.
Using yeast to help
One method involves treating plants like tree nuts and corn with a special type of yeast called Pichia anomala. This yeast can reduce the growth of A. flavus. For example, treating pistachio trees with P. anomala stopped A. flavus growth by up to 97% compared to untreated trees. The yeast works by competing with A. flavus for space and food, which limits how much the harmful fungus can grow.
A helpful type of A. flavus
The good news is that not all types of A. flavus are harmful. There's a special strain called AF36 that doesn't produce toxins. This helpful strain is used in pesticides to protect crops.
AF36 is grown on sterile seeds, which act as a carrier and provide food for the fungus. When these seeds are spread on cotton and corn fields, the AF36 fungus grows and spreads. It then competes with the harmful, toxin-producing types of A. flavus. This means the good AF36 takes over the space and food, preventing the bad strains from growing and making aflatoxins. Wind and insects help spread the non-toxic AF36 spores even further.
- How safe is mouldy food to eat? BBC News magazine. [1]
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Aspergillus flavus para niños
In Spanish: Aspergillus flavus para niños
 | Bayard Rustin |
 | Jeannette Carter |
 | Jeremiah A. Brown |


