Balancing selection facts for kids
Balancing selection is a cool idea in natural selection. It's how different versions of a gene (called alleles) stay common in a group of living things, instead of one version completely taking over. This often happens when having two different versions of a gene is actually better for survival than having two of the same version. This helps keep lots of different traits (called genetic polymorphism) alive in a population.
Scientists like Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace noticed that wild animals and plants are super varied. Modern research also shows that having lots of different genes is very common in populations where individuals can mate freely.
There are a few ways balancing selection works to keep these different gene versions around. The two main ones are called heterozygote advantage and frequency-dependent selection.
Contents
How Balancing Selection Works
What is Heterozygote Advantage?
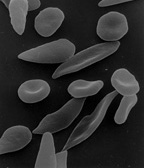
In heterozygote advantage, an individual who has two different versions of a gene at a specific spot (called a locus) is stronger or healthier than someone who has two identical versions. When this happens, the different gene versions stay "balanced" in the population.
A famous example is sickle cell anemia in humans. This is a disease that affects red blood cells. If a person inherits the sickle cell gene (HgbS) from both parents, their red blood cells can become sickle-shaped, which causes serious health problems and a shorter life.
However, if a person inherits one sickle cell gene (HgbS) from one parent and a normal gene (HgbA) from the other, they usually have a normal life. These individuals are also resistant to the malarial parasite. Malaria is a disease that kills many people each year. Because people with one sickle cell gene are protected from malaria, this gene stays common in places where malaria is a big problem. This is because having one copy of the gene is an advantage.
What is Frequency-Dependent Selection?
Frequency-dependent selection happens when how "fit" or successful a certain trait is depends on how common it is.
In positive frequency-dependent selection, a trait becomes more successful as it gets more common. But in negative frequency-dependent selection, a trait becomes more successful when it is less common.
For example, imagine a predator that hunts snails. If most snails have a plain shell, the predator might learn to look for plain shells. If a few snails have striped shells, the predator might not notice them as much, making the striped snails more successful. But if striped snails become very common, the predator might start looking for them instead. This helps keep both plain and striped snails in the population.
When Fitness Changes Over Time and Place
Sometimes, how successful a gene version is can change a lot depending on the stage of life (like a larva versus an adult) or in different parts of an habitat. A gene that is good in one place might not be good in another.
When Selection Depends on Others
The success of a gene version can also depend on what other individuals in the population are doing. For example, if everyone in a group is doing one thing, it might be better for an individual to do something different to survive and reproduce.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Selección disruptiva para niños
In Spanish: Selección disruptiva para niños
 | William L. Dawson |
 | W. E. B. Du Bois |
 | Harry Belafonte |





