Bean machine facts for kids
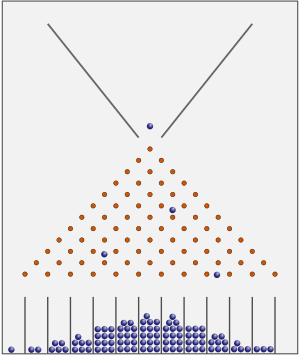
The bean machine, also known as the Galton box or quincunx, is a clever machine. It was invented by Sir Francis Galton, a famous scientist, to show how things often spread out in a very natural way. This spreading out is called the normal distribution, or sometimes the "bell curve."
The machine is a tall, flat board with many rows of small pins arranged in a pattern. When you drop tiny balls from the top, they fall down. As they hit the pins, they bounce either left or right. Each time a ball hits a pin, it has an equal chance of going left or right. Eventually, all the balls land in narrow bins at the very bottom.
What's amazing is that after many balls have fallen, the height of the balls in the bins forms a shape like a bell. This bell shape shows the normal distribution. It means that most balls end up in the middle bins, and fewer balls end up in the bins further to the sides.
You can even see how Pascal's triangle relates to the pins! It shows how many different paths a ball can take to reach each pin. A very large working model of this machine can be found at the Museum of Science in Boston.
How the Bean Machine Works
The bean machine is a great way to understand how chance and probability work together. Imagine a tiny ball starting its journey at the top. It falls and hits the first pin. It can go left or right. Then it hits another pin, and again, it can go left or right. This happens over and over as it falls through many rows of pins.
Each bounce is like a tiny decision. Because there are so many pins and so many bounces, the balls don't all go to one side. They spread out. Most of the time, a ball will have roughly an equal number of left and right bounces, making it land near the center. Only a few balls will have many more left bounces than right, or vice versa, making them land at the edges.
Understanding the Bell Curve
The "bell curve" is a special shape that shows up in many places in nature and science. It's also called the normal distribution. When you look at the balls in the bins of the Galton box, you see this shape. The tallest pile of balls is in the middle bin. The piles get shorter and shorter as you move away from the center.
This shape tells us that the most common outcome is the one in the middle. Outcomes that are very different from the average are much less likely. For example, if you measure the heights of many people, most people will be around the average height. Only a few people will be very tall or very short. The bean machine shows this idea in a simple, visual way.
Images for kids
-
The quincunx, as drawn by Sir Francis Galton
See also
 In Spanish: Máquina de Galton para niños
In Spanish: Máquina de Galton para niños