Bernardino Ramazzini facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Bernardino Ramazzini
|
|
|---|---|

Bernardino Ramazzini
|
|
| Born | 4 October 1633 Carpi
|
| Died | 5 November 1714 (aged 81) |
| Nationality | Italian |
| Alma mater | University of Parma |
| Known for | cinchona, occupational medicine |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | medicine |
| Institutions | University of Modena, University of Padua |
Bernardino Ramazzini (born October 4, 1633 – died November 5, 1714) was an important Italian doctor. He is often called the "father of occupational medicine." This means he was one of the first people to study how different jobs can affect a person's health.
Ramazzini also supported using cinchona bark to treat malaria. Cinchona bark is where the medicine quinine comes from. His most famous work was a book called De Morbis Artificum Diatriba, which means "Diseases of Workers."
Contents
About Bernardino Ramazzini
Ramazzini was born in a town called Carpi, Italy, on October 4, 1633. He studied medicine at the University of Parma. This is where he first became interested in how people's jobs could make them sick.
Ramazzini's Career
In 1682, Ramazzini became a professor at the University of Modena. Later, in 1700, he moved to the University of Padua and taught medicine there until he passed away.
His important book, De Morbis Artificum Diatriba, was first published in 1700. A second edition came out in 1713.
Studying Job-Related Illnesses
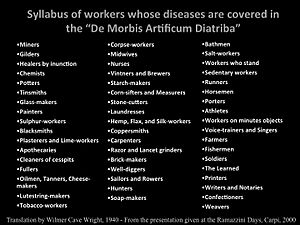
Ramazzini's book, De Morbis Artificum Diatriba (Diseases of Workers), looked at the health dangers in over fifty different jobs. He wrote about how things like chemicals, dust, metals, repeated movements, and strange body positions could harm workers. This book was a huge step in starting the field of occupational medicine.
He suggested that doctors should always ask their patients, "What is your job?" This simple question helped doctors understand if a patient's work was making them ill.
Ramazzini believed that preventing illness was much better than trying to cure it. He once said, "it is much better to prevent than to cure, and so much easier to foresee future harm and avoid it rather than have to get rid of it after having fallen prey."
Treating Malaria
Ramazzini was also one of the first doctors to strongly support using cinchona bark to treat malaria. Many people at the time thought quinine was harmful or didn't work. But Ramazzini knew how important it was. He famously said, "It [quinine] did for medicine what gun powder did for war."
Later Life and Legacy
Bernardino Ramazzini passed away in Padua on November 5, 1714.
His work is still remembered today. For example, a writer once mentioned Ramazzini's early studies when talking about how sitting too much can be bad for your health.
An honor society for health professionals, called the Collegium Ramazzini, is named after him.
Works
See also
 In Spanish: Bernardino Ramazzini para niños
In Spanish: Bernardino Ramazzini para niños