Bombus citrinus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Bombus citrinus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Apidae |
| Genus: | Bombus |
| Subgenus: | Psithyrus |
| Species: |
B. citrinus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Bombus citrinus (Smith, 1854)
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Bombus citrinus is a type of bumblebee often called the lemon cuckoo bumblebee. It gets this name because of its bright lemon-yellow color. This bee lives in eastern North America.
It's a special kind of bumblebee known as a cuckoo bumblebee. This means it doesn't build its own nest. Instead, it takes over the nests of other bumblebees. The lemon cuckoo bumblebee replaces the original queen and then makes the worker bees care for its own young. Its main host bees are the common eastern bumblebee (Bombus impatiens) and the half-black bumblebee (B. vagans).
Before a female lemon cuckoo bumblebee takes over a nest, she flies around. She visits many different plants to find food. These plants include asters, thistles, snakeroots, blazing-stars, mountain-mints, and goldenrods.
Contents
What is a Cuckoo Bumblebee?
How Bombus citrinus is Unique
Bombus citrinus belongs to a special group of parasitic bumblebees called Bombus subgenus Psithyrus. Long ago, Psithyrus was thought to be its own separate group. So, this bee was once called Psithyrus citrinus.
Bees in the Psithyrus group are different from other bumblebees. They have a thick abdomen (the back part of their body) and a long stinger. Their jaws are also bigger. Unlike other bumblebees, they don't have pollen baskets on their legs. They also don't have worker bees in their group. These features help them take over other bee nests.
Bombus citrinus is closely related to Bombus insularis and Bombus variabilis. These cuckoo bees have changed over time to be good at taking over specific host nests. This is a type of coevolution, where two species evolve together.
What Does It Look Like?
Physical Features of the Lemon Cuckoo Bumblebee
Like all cuckoo bumblebees, the lemon cuckoo bumblebee has special hind legs. The outer part of their back legs is rounded and very hairy. It's not flat like the legs of other bumblebees that carry pollen.
Their heads are shaped a bit like a teardrop. Most of their body, especially the chest area (thorax), is yellow. This yellow color can sometimes go down to the fifth segment of their abdomen. The hairs on their face are usually black, but some yellow hairs might be mixed in. You usually won't see black hairs on their chest, and there's no black band between their wings.
The hairs on their abdomen are short and even. The hairs on the fifth segment are longer than on other parts. Their wings are a bit see-through. They can be reddish-brown to brownish-black. When they are young, their wings might look yellowish. Sometimes, black hairs are mixed in with the yellow ones.
Where Does It Live?
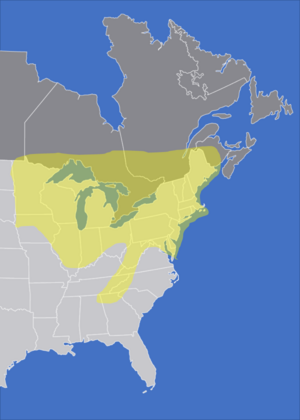
The lemon cuckoo bumblebee is found in parts of northeastern North America. Its home range includes eastern and central parts of Canada. It also lives in northeastern U.S. states. You can find it in some mid-western and southeastern regions of the U.S. as well.
How Does It Live?
Taking Over a Nest: The Cuckoo Bee's Strategy
Bombus citrinus is a social parasite. This means it relies completely on other bee species to raise its young. It targets the nests of Bombus impatiens and Bombus vagans.
The cuckoo bee finds a host nest by following chemical smells left by the host workers. Once it finds a nest, it might visit it a few times. This helps the cuckoo bee decide if the nest is good for taking over.
When the cuckoo bee tries to enter, host workers might attack it. But sometimes, the cuckoo bee can sneak in. It does this by blending in with the host bees' chemical smells. Once inside, the female Bombus citrinus will take over the host queen's role.
To show its power over the host workers, the cuckoo bee acts aggressively. It might rub its body against the host workers. It also grabs them with its jaws and front legs. It might even make motions as if to sting them. By doing this, the cuckoo bee shares its own chemical smells with the host workers. This also stops the host workers from laying their own eggs. The eggs laid by the female Bombus citrinus will then be cared for by the host workers.