Brüggen Glacier facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Brüggen Glacier |
|
|---|---|
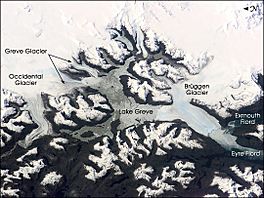
Brüggen Glacier and surrounding area, September 2001
|
|
| Type | Tidewater glacier |
| Location | Chile |
| Coordinates | 49°13′S 74°00′W / 49.217°S 74.000°W |
| Area | 1,265 km2 (488 sq mi) |
| Length | 66 km (41 mi) |
| Terminus | Sealevel |
| Status | Advancing |
The Brüggen Glacier, also known as the Pío XI Glacier, is a huge ice river in southern Chile. It is the largest glacier that flows out from the western side of the Southern Patagonian Ice Field.
This amazing glacier is about 66 km (41 mi) long. This makes it the longest glacier in the Southern Hemisphere, not counting Antarctica.
Most glaciers around the world are shrinking. But the Brüggen Glacier is special because it grew a lot between 1945 and 1976. It pushed forward about 5 km (3.1 mi) across the Eyre Fjord. By 1962, it reached the western shore. This movement cut off Lake Greve from the sea. The glacier kept growing both north and south in the fjord. It added almost 60 square kilometres (23 sq mi) of ice. The glacier is named after a German geologist, Juan Brüggen Messtorff.
See also
 In Spanish: Glaciar Pío XI para niños
In Spanish: Glaciar Pío XI para niños
- Bernardo O'Higgins National Park
- Lautaro (volcano)
- List of glaciers


