Cactus mouse facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Cactus mouse |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Cricetidae |
| Subfamily: | Neotominae |
| Genus: | Peromyscus |
| Species: |
P. eremicus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Peromyscus eremicus (Baird, 1858)
|
|
 |
|
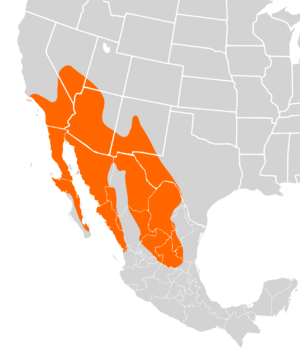
| Cactus mouse range in North America | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The cactus mouse (Peromyscus eremicus) is a small rodent that lives in the deserts of western North America. It's also sometimes called the cactus deermouse. These mice belong to a group called "deermice" and are known for living in dry, hot places.
Contents
What Do They Look Like?
Cactus mice are small rodents with big eyes and ears. They have a pointy nose and a long tail that is usually one color. Their tails are often as long as or even longer than their bodies. Unlike many other mice, their tails are almost bare, not very furry. Their feet also have bare soles.
Their fur is soft and can be different shades of brown, from light tan to a cinnamon color. Their bellies are white. Young mice often look a bit grayer than their parents.
Most cactus mice live for about one year in the wild. But if they live in a safe place like a lab, they can live much longer, sometimes over seven years!
Here are some average sizes for a cactus mouse:
- Total length (from nose to tail tip): 16 to 21 centimeters (about 6 to 8 inches)
- Body length: 7 to 10 centimeters (about 3 to 4 inches)
- Tail length: 8 to 12 centimeters (about 3 to 5 inches)
- Weight: 18 to 40 grams (about 0.6 to 1.4 ounces)
Female cactus mice are usually a bit bigger than males.
Where Do They Live?
Cactus mice live in dry, desert areas. You can find them in the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. They also live on islands off the coast of the Baja California peninsula and in the Gulf of Mexico.
They prefer places with warm temperatures. Very cold weather might stop them from spreading further north. These mice share their homes with other types of deermice, like the California mouse and the canyon mouse.
What Do They Eat?
Cactus mice eat many different things. Their diet includes seeds, mesquite beans, and small fruits from hackberry trees. They also enjoy eating insects and green plants.
Their diet changes with the seasons:
- Winter: They eat more insects.
- Spring: They mostly eat seeds and flowers.
- Summer: They eat seeds, leafy greens, and insects.
- Autumn: They start eating more insects again, getting ready for winter.
How Do They Behave?
Cactus mice are mostly active at night (this is called nocturnal behavior). Sometimes, you might see them around dawn or dusk (this is called crepuscular behavior). They might be less active when the moon is full and bright.
People who have handled them say they are shy and easily startled. They usually don't bite when picked up. If they get scared, they make a loud, high-pitched squeak. In studies, cactus mice can run quite fast, averaging about 8 miles per hour!
Cactus mice have a special way of dealing with hot, dry places. Their bodies use less energy than many other mice. This helps them survive when there isn't much food or water. They can even go into a deep sleep called torpor if they don't have enough food, especially in winter. This helps them save energy.
These mice are important in their environment. They help spread seeds by eating them and are also a food source for other animals.
Family Life
Scientists don't know a lot about how cactus mice mate. But based on other deermice, they likely have many partners. They can have babies all year round, but they tend to mate more often in warmer months. Female mice can start having babies when they are about two months old.
Cactus Mice and People
Cactus mice are good animals for scientists to study in laboratories. They are clean, live well in captivity, and have many babies. This makes them useful for learning about how bodies work and about genetics.
These mice do not cause any known problems for humans or our activities. Sometimes, mice can carry certain germs. While some cactus mice have been found with a virus called hantavirus, it's not common for this specific mouse to spread it widely.
Images for kids
-
A male cactus mouse in a jar with a peanut on his head. This mouse was found in a house in Albuquerque.
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |



