Candida albicans facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Candida albicans |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
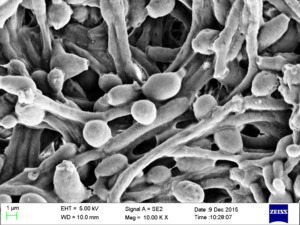
| Candida albicans visualized using scanning electron microscopy. Note the abundant hyphal mass. | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Saccharomycetes |
| Order: | Saccharomycetales |
| Family: | Saccharomycetaceae |
| Genus: | Candida |
| Species: |
C. albicans
|
| Binomial name | |
| Candida albicans (C.-P. Robin) Berkhout (1923)
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
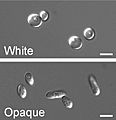
Candida albicans is a tiny living thing called a yeast. It is a common part of the human body, especially in the gut and mouth. About 40 to 60 out of every 100 healthy adults have C. albicans in their bodies. This yeast can also live outside the human body.
Usually, C. albicans lives peacefully with us and doesn't cause problems. This is called being a commensal organism. But sometimes, if a person's body defenses (their immune system) are weak, C. albicans can grow too much. When this happens, it can cause an infection called candidiasis. This infection is often seen in people who are very sick or have weakened immune systems.
C. albicans is one of the main types of Candida yeast that cause infections in humans. Other types like C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, and C. glabrata also cause these infections. Together, these yeasts are responsible for most cases of candidiasis.
Contents
What is Candidiasis?
Candidiasis is an infection caused by too much Candida yeast. It can happen in different parts of the body. For example, it can affect the skin, mouth, throat, or private areas. In some serious cases, it can even get into the blood.
How Candida Can Cause Problems
Candida yeasts are found all over the world. They most often cause infections in people whose bodies are already fighting other serious illnesses. These people have a weaker immune system.
Candida is one of the most common causes of infections that people get while in the hospital. Patients who have recently had surgery, received an organ transplant, or are in intensive care units (ICU) are at higher risk. C. albicans is the top cause of fungal infections in these very sick patients.
How Candida Spreads
Candida can spread in a few ways:
- From a mother to her baby during childbirth.
- From person to person, especially in hospitals. For example, healthcare workers can sometimes spread the yeast to patients who have weak immune systems.
Common places where Candida infections happen include the skin, mouth, throat, and private areas. Sometimes, in very sick people, the infection can spread to the blood. When this happens, it is called a systemic fungal infection. These types of infections can be very serious for people with weakened immune systems.
C. albicans often forms groups of cells called biofilms inside the body. These biofilms can make the infection harder to treat.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Candida albicans para niños
In Spanish: Candida albicans para niños
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |