Carrying capacity facts for kids
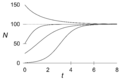
In biology, the carrying capacity is the largest number of living things that an environment can support. Think of it as the maximum number of animals or plants that can live in a certain area without running out of important things like food, water, or space.
Every place has a limited amount of resources. These resources, like food and shelter, decide how many living things can survive there. For example, a small forest can only feed a certain number of deer. If too many deer live there, they might eat all the plants, and then some deer won't have enough to eat.
Sometimes, things happen that change the carrying capacity. A forest fire, for instance, can destroy many plants and trees. This means there's less food and shelter for animals, so the forest can support fewer of them. This lowers the carrying capacity.
If too many living things are in an environment, it's called overpopulation. This can cause problems because there aren't enough resources for everyone.
What is Carrying Capacity?
The idea of "carrying capacity" first helped people figure out how many animals could graze on a piece of land. Now, we use this idea to understand how many humans an area or even the Earth can support.
How Carrying Capacity Changes
The carrying capacity of an environment is not always the same; it can change over time. Humans can have a big impact on it. For example, agriculture and irrigation (watering crops) help us grow more food. This allows more people to live in an area than before.
However, some human activities can also lower the carrying capacity. Pollution can make water or air unsafe, reducing the number of living things an area can support. Using too many natural resources can also make it harder for an environment to support life.
Images for kids
-
A fishery at sunset in Cochin, Kerala, India.
See also
 In Spanish: Capacidad de carga para niños
In Spanish: Capacidad de carga para niños