Casimir effect facts for kids
The Casimir effect is a strange force that pulls two metal plates together when they are very close in a vacuum (empty space). A scientist named Hendrik Casimir first thought of this idea in 1948. This tiny pull happens because of something called the quantum uncertainty principle, which describes how tiny particles behave.
Contents
What is the Quantum Uncertainty Principle?
The quantum uncertainty principle is a basic rule in physics. It says that you cannot know everything perfectly about a tiny particle at the same time. For example, if you know exactly where a particle is, you can't know its exact speed. And if you know its exact speed, you can't know its exact location.
This rule also applies to "empty" space. You might think empty space has nothing in it. But according to quantum physics, even empty space is full of tiny, quick changes. These changes are like invisible, super-fast "virtual particles" that pop in and out of existence all the time. We can't see these virtual particles directly. However, we can see the small effects they have on real objects.
How Virtual Particles Cause the Casimir Effect
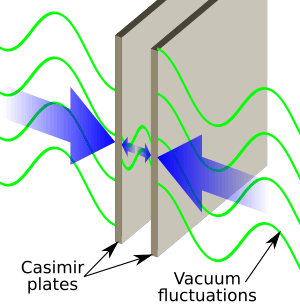
Some of these virtual particles are like tiny waves of light, called virtual photons. Imagine these waves bouncing around.
- Outside the plates: In the wide-open space outside the two metal plates, all kinds of virtual waves can exist. They can have any wavelength (the distance between two peaks of a wave).
- Between the plates: Inside the tiny gap between the two metal plates, things are different. Only certain virtual waves can fit in this small space. Think of it like a guitar string: only certain notes (wavelengths) can be played on it. Waves that don't fit perfectly will cancel themselves out. This means there are fewer virtual waves bouncing around inside the plates compared to the outside.
Because there are more virtual particles pushing on the outside of the plates than on the inside, the plates are gently pushed towards each other. This is the Casimir effect! It's a tiny force, but it's real.
Energy in Empty Space
This effect also tells us something interesting about energy. In normal empty space, the total energy is considered to be zero. This is because every particle has positive energy, but its gravity creates negative energy that balances it out.
Since there are fewer virtual particles between the plates, the energy density (how much energy is in a certain space) between the plates is actually less than zero. It's like having "negative energy" compared to regular empty space. This idea of negative energy is very important in advanced physics.
See also
 In Spanish: Efecto Casimir para niños
In Spanish: Efecto Casimir para niños
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |