Cataplexy facts for kids
Cataplexy is a medical condition where a person's muscles suddenly become weak or limp. This happens when they feel strong emotions like laughter, fright, anger, or sadness. People with cataplexy might feel their muscles suddenly fail them.
Cataplexy often affects people who have narcolepsy. Narcolepsy is a sleep disorder where people suddenly fall asleep without being able to control it. Cataplexy is sometimes confused with epilepsy. Epilepsy causes seizures that might look similar, but they are caused by different things.
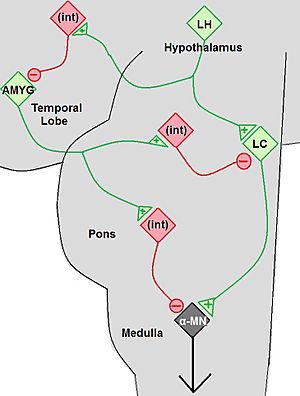
Cataplexy is a sudden, short episode of muscle weakness. During an attack, a person is fully awake and aware of what is happening. It is caused by a problem with a brain chemical called hypocretin (also known as orexin). This chemical helps control how awake and alert you feel. Cataplexy without narcolepsy is very rare, and its cause is not fully known.
The word "Cataplexy" comes from the Greek words kata, meaning "down," and plexis, meaning "a stroke or seizure."
Contents
What Does Cataplexy Look Like?
Cataplexy shows up as muscle weakness. This can be very slight, like a small slackening of the face muscles. It can also be very strong, causing complete muscle paralysis and making a person fall down.
How Long Do Attacks Last?
Attacks are usually short. Most last from a few seconds to a couple of minutes. They often involve the jaw dropping, the neck becoming weak, or the knees buckling. Even if someone falls, they can usually avoid getting hurt. This is because they often feel an attack coming. The fall is usually slow and gentle.
What Happens During an Attack?
During an attack, a person's speech might become slurred. Their vision might also be affected, causing double vision or making it hard to focus. However, their hearing and awareness stay normal. They know what is happening around them.
Cataplexy attacks stop on their own. They do not need medical help to end. If the person is lying down comfortably, they might become sleepy. They could also have vivid dreams just before falling asleep, or quickly enter REM sleep.
What Triggers Cataplexy?
Cataplexy gets worse when a person is tired. However, it is different from the sudden sleep attacks of narcolepsy. Cataplexy is usually triggered by strong emotions. These can include laughter, anger, surprise, awe, and embarrassment. It can also be triggered by sudden physical effort, especially if the person is caught off guard.
For example, at the 1968 Summer Olympics, long jump athlete Bob Beamon had a cataplectic attack. This happened when he realized he had broken the world record by a lot! Sometimes, cataplectic attacks can happen without any clear emotional trigger.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Cataplexy?
Doctors usually diagnose narcolepsy and cataplexy based on a person's symptoms. If someone has four main symptoms, it strongly suggests narcolepsy. These symptoms are:
- Feeling very sleepy during the day.
- Muscle paralysis when falling asleep.
- Vivid dreams or hallucinations when falling asleep.
- Cataplexy symptoms.
A special test called a Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT) is often done. This test helps doctors measure how sleepy a person is during the day.
How is Cataplexy Treated?
Cataplexy is treated with medications. There are no treatments that involve changing behavior. People with narcolepsy often try to avoid thoughts and situations that might cause strong emotions. This is because they know these emotions can trigger cataplectic attacks.
See also
 In Spanish: Cataplexia para niños
In Spanish: Cataplexia para niños

