Commonwealth Telecommunications Organisation facts for kids

Logo of the Commonwealth Telecommunications Organisation
|
|
| Abbreviation | CTO |
|---|---|
| Formation | 11 May 1948 |
| Type | International organization |
| Purpose | Telecommunications |
| Headquarters | London, United Kingdom |
|
Area served
|
Commonwealth of Nations |
|
Membership
|
33 full state members |
|
Secretary-General
|
Bernadette Lewis |
The Commonwealth Telecommunications Organisation (CTO) is a group that helps countries and companies work together on technology. It focuses on information and communication technology (ICT), which includes things like the internet, phones, and computers.
The CTO was officially started in London on May 11, 1948. It was formed by an international treaty called the Commonwealth Telegraphs Agreement. This agreement was signed by many Commonwealth countries.
Contents
What the CTO Does
The CTO connects governments and other groups. Its main goal is to improve how people communicate using technology. This means making sure everyone can access and use things like the internet and mobile phones. They help countries share ideas and learn from each other about new technologies.
A Look at CTO's History
Early Beginnings
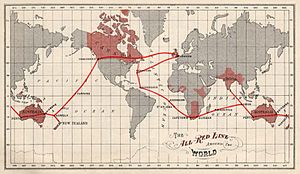
Before the CTO, there was a group called the Pacific Cable Board. This group was created in 1901. Its job was to build and manage a huge telegraph system. This system was known as the All Red Line. It connected different parts of the British Empire using underwater cables. Imagine it like an early version of the internet, but for sending messages by telegraph!
Forming the CTO
As many countries in the British Empire became independent, a new plan was needed. The old system had to be updated to share costs and responsibilities fairly. So, in 1948, the Commonwealth Telegraph Agreement was signed. This agreement created the Commonwealth Telecommunications Organisation. It replaced the older Pacific Cable Board. The CTO was designed to help Commonwealth nations work together on communication in a new way.
Who Are the Members?
The CTO has many members from around the world. These include both countries and technology companies.
Country Members
There are 33 countries that are full members of the CTO. These countries are part of the Commonwealth. Some examples include India, Nigeria, South Africa, and the United Kingdom. There are also some smaller areas that are "affiliate" members, like Bermuda and Gibraltar.
Technology Company Members
Many big technology companies are also members of the CTO. They work with the organization to share their knowledge and help improve communication for everyone. Some well-known companies that are members include:
- Avanti Communications
- British Telecom
- Huawei
- Intelsat
- PwC London
- Safaricom
- Vodafone
These companies help the CTO achieve its goals by providing expertise and resources in the world of information and communication technology.

