Earthquake performance simulation facts for kids
Earthquake performance simulation is a way for engineers to study how buildings and other structures react during an earthquake. It helps them see what might happen without waiting for a real earthquake to strike. This helps make buildings safer and stronger.
How Engineers Simulate Earthquakes
Engineers use special methods to test how buildings will stand up to earthquakes. They can either shake real models of buildings or use powerful computers to predict what will happen. This helps them design safer buildings for everyone.
Shaking Things Up: Physical Tests
One of the best ways to test a building's strength against an earthquake is to use a shake-table. Imagine a giant table that can shake just like the ground does during an earthquake! Engineers place a model of a building on this table. Then, they make the table shake with forces similar to a real earthquake. This lets them watch exactly what happens to the building model.
These kinds of tests help engineers see weak spots in designs. The very first experiments like this happened over 100 years ago. It's a great way to learn without having to wait for a real earthquake to happen.
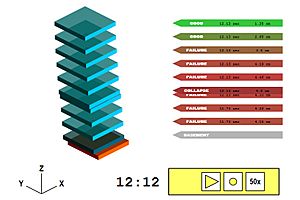
Computers to the Rescue: Digital Tests
Another way to test buildings is by using computers. This is called computational earthquake performance simulation. Engineers create a detailed digital model of a building on a computer. Then, they use special programs to apply earthquake forces to this digital model.
At first, these computer tests were quite simple. They would apply steady sideways pushes, like a strong wind. This was based on how much the ground might shake. But as computers became much more powerful, engineers could do more complex tests. Now, they can simulate the actual shaking and movement of an earthquake over time. This helps them understand how a building will react to different kinds of earthquake motions.