Electrical filament facts for kids
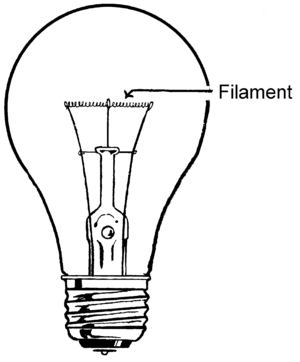
A light bulb has a tiny, thin wire inside it. This special wire is called a filament. It's the part of the light bulb that actually glows and makes light!
Contents
What is a Light Bulb Filament?
A filament is a very thin wire found inside an incandescent light bulb. It is held in place by two thicker wires. When you turn on the light, electricity flows through this thin wire. This makes the filament get very hot and glow brightly.
How Filaments Work
When electric current passes through the filament, it heats up a lot. This heat makes the filament glow, producing light. To make the bulb shine even brighter, the filament is often made into a tiny coil. This is like a spring made of very fine wire. It's called a "coiled coil." This design helps the bulb produce more light from a smaller space.
Materials Used for Filaments
Most filaments in incandescent light bulbs are made from a strong metal called tungsten. Tungsten is chosen because it can get extremely hot without melting. It also glows very brightly when heated. Early light bulbs used different materials, like carbon, but tungsten became the standard because it works so well.
Images for kids
-
Original carbon-filament bulb from Thomas Edison's shop in Menlo Park
-
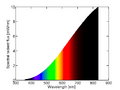
Spectrum of an incandescent lamp at 2200 K, showing most of its emission as invisible infrared light.
-
Xenon halogen lamp with an E27 base.
-
The 1902 tantalum filament light bulb was the first one to have a metal filament. This one is from 1908.
-
Close-up of a tungsten filament inside a halogen lamp.
See also
 In Spanish: Filamento (electricidad) para niños
In Spanish: Filamento (electricidad) para niños