Amur hedgehog facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Amur hedgehog |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| In Lazo national park, Russia | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Erinaceus
|
| Species: |
amurensis
|
 |
|
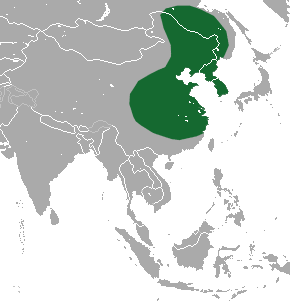
| Amur hedgehog range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
The Amur hedgehog (Erinaceus amurensis), also called the Manchurian hedgehog, is a spiny mammal. It looks and acts much like the European hedgehog. However, it has slightly lighter fur. These hedgehogs live in parts of Russia, China, and the Korean Peninsula. Like other hedgehogs, they use their excellent sense of smell and hearing to find food. The name "hedgehog" comes from the pig-like grunts they make while searching for food.
| Top - 0-9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
What is an Amur Hedgehog?
This hedgehog is a close relative of the European hedgehog. It is a bit bigger and lighter in color. An Amur hedgehog's body is usually about 16 to 29 centimeters (6 to 11 inches) long. It has a very short tail. These hedgehogs typically weigh between 600 and 1000 grams (about 1.3 to 2.2 pounds).
Spines and Defense
The head, back, and sides of the Amur hedgehog are covered with long, sharp spines. These spines are not all the same color. Some are plain white. Others have a white or yellowish-brown base and tip. Their middle part is a medium to dark brown. This mix of colors gives the hedgehog a pale, brownish-grey look.
The spines on their head are separated by small areas of bare skin. These spines are very strong. They are made of a tough material called keratin. This means they do not break or fall out easily.
Hedgehogs use their spines to protect themselves. When they feel threatened, they curl up into a tight ball. This makes their sharp quills stick out in every direction. Their face and soft belly are tucked safely inside.
The face and underside of the Amur hedgehog are covered in soft, pale hair.
Where Do Amur Hedgehogs Live?
Amur hedgehogs are found naturally in several places. These include the Amur Oblast and Primorye regions of Russia. They also live in Manchuria in China and across the Korean Peninsula. Their home range stretches from south of the Yangtze River up to the Amur Basin.
Hedgehog Homes
These hedgehogs can live in many different types of places. They are found in grasslands and at the edges of forests. They also like areas with mixed forests, which have both pine trees and leafy trees.
Some experts say they prefer valleys and lowlands. They are not usually found in high mountain areas or large farm fields. However, other sources suggest they can live in mountains and steppes. They are also seen in shrublands, cultivated lands, villages, and city parks.
Amur hedgehogs were also brought to some parts of Japan. They now live in the Kanagawa and Shizuoka Prefectures.
Amur Hedgehog Life
Amur hedgehogs are mostly solitary animals. This means they live on their own. They usually only come together during the mating season. There is not much specific information known about how this particular species reproduces.
What Do They Eat?
Like most hedgehogs, the Amur hedgehog is a nocturnal animal. This means it is active at night. They come out after dark to search for food. Their diet mainly includes small insects and other tiny creatures. They especially like fly larvae and earthworms. They also eat centipedes, snails, mice, and frogs. Sometimes, they might even eat fruit.
Hibernation
Amur hedgehogs usually have one or two litters of babies in the summer. Each litter can have four to six young hedgehogs. Around October, when the weather gets cold, the hedgehog goes into a deep sleep. This is called torpor or hibernation. They stay asleep until spring arrives.
Conservation Status
The Amur hedgehog is a common species. Experts have not found any major threats to its survival. Because of this, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) lists its conservation status as "least concern." This means they are not currently at risk of disappearing.
In captivity, these hedgehogs can live for about 8 years. It is not known exactly how long they live in the wild.


