Extracellular fluid facts for kids
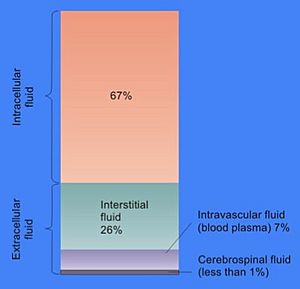
Extracellular fluid is the body fluid found outside of your cells. It makes up about one-third (1/3) of all the water in your body. Think of it as the watery environment that surrounds your cells, helping them stay healthy and do their jobs.
What It's Made Of
The extracellular fluid (ECF) is mostly made of two main parts:
- Interstitial fluid: This is the fluid that surrounds all your body cells, like a tiny ocean they live in. It's the biggest part of the ECF.
- Blood plasma: This is the liquid part of your blood. It carries blood cells, nutrients, and waste products throughout your body.
These two parts, interstitial fluid and plasma, make up about 97% of all the ECF. A small amount of ECF is also lymph, which is part of your body's immune system.
The rest of the ECF is called transcellular fluid. This special fluid is found in specific places, like:
- The aqueous humour in your eyes, which helps keep them shaped.
- The synovial fluid in your joints, which helps them move smoothly.
- The cerebrospinal fluid around your brain and spinal cord, protecting them.
- Fluids in your digestive system, like saliva and gastric juice.
- Fluids in your inner ear, called perilymph and endolymph.
In a typical young adult, about 14 liters (or 20% of their body weight) is extracellular fluid. About 11 liters of this is interstitial fluid, and 3 liters is blood plasma.
How It Works
The extracellular fluid is super important because it's where all the action happens between your cells and the rest of your body. It acts like a delivery and waste removal system.
Here's what the ECF does:
- Carries important stuff: It contains things like dissolved gases (like oxygen), nutrients (from your food), and electrolytes (like salt) that your cells need to survive. These substances dissolve in the ECF and are transported to where they are needed.
- Helps cells communicate: Cells can release substances into the ECF. Some of these substances might be signals for other cells, while others might form structures outside the cells.
- Forms the "filler" material: Some materials released by cells into the ECF can come together to form strong fibers, like collagen. These fibers, along with other substances, create the extracellular matrix. Think of the extracellular matrix as the "glue" or "filler" substance that holds cells together and gives tissues their shape and strength throughout your body. All these structures are surrounded by the ECF, but they are not part of the fluid itself.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Fluido extracelular para niños
In Spanish: Fluido extracelular para niños
 | Valerie Thomas |
 | Frederick McKinley Jones |
 | George Edward Alcorn Jr. |
 | Thomas Mensah |