Finnic languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Finnic |
|
|---|---|
| Balto-Finnic | |
| Ethnicity: | (Balto-)Finnic |
| Geographic distribution: |
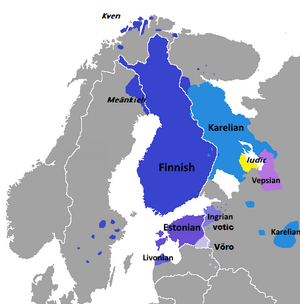
Northern Fennoscandia, Estonia, Northwestern Russia, Latvia (extinct) |
| Linguistic classification: | Uralic
|
| Proto-language: | Proto-Finnic |
| Subdivisions: |
Eastern Estonian–Votic
Livonian (extinct)
South Estonian
|
 |
|
The Finnic languages are a group of languages. They are also called Balto-Finnic languages. They belong to the larger Uralic languages family. These languages are spoken in Northeastern Europe. You can find speakers around the Baltic Sea. The main countries are Finland, Estonia, and parts of Northwestern Russia. The two most widely spoken Finnic languages are Estonian and Finnish.
Contents
What are Finnic Languages?
The Finnic languages are a branch of the Uralic languages. This family includes languages like Hungarian and Sami. Finnic languages are spoken by millions of people. Most speakers live in Finland and Estonia.
Where are Finnic Languages Spoken?
These languages are mainly found in Northern Europe. This area includes Finland, Estonia, and parts of Russia. Some Finnic languages are also spoken in Sweden and Norway. This shows their historical spread.
Main Finnic Languages
The two biggest Finnic languages are Finnish and Estonian.
- Finnish: This is the official language of Finland. It is spoken by over 5 million people.
- Estonian: This is the official language of Estonia. About 1.1 million people speak it.
Other Finnic languages are smaller. Some are even endangered or extinct. For example, Livonian is almost extinct.
How are Finnic Languages Related?
All Finnic languages come from a common ancestor. This ancient language is called Proto-Finnic. Over thousands of years, Proto-Finnic split into different languages. This is how Finnish, Estonian, and others developed. They share many similar words and grammar rules.
Similarities and Differences
Finnic languages have many things in common. They often use suffixes instead of prepositions. This means they add endings to words. For example, in Finnish, "in the house" is "talossa". "Talo" means house, and "ssa" means in.
However, there are also differences. The sounds of the languages can vary. Their vocabularies have changed over time. This is due to contact with other languages. For example, Finnish has many words from Swedish. Estonian has words from German.
History of Finnic Languages
The history of Finnic languages goes back thousands of years. Scientists believe Proto-Finnic was spoken around 2,000 to 2,500 years ago. People then started to move and separate. This led to new languages forming.
Early Development
The first speakers of Proto-Finnic lived near the Baltic Sea. They were likely hunter-gatherers. As communities grew, they spread out. This geographic separation caused language changes. Different dialects slowly became distinct languages.
Influence from Other Languages
Finnic languages have been influenced by their neighbors. They borrowed words from Germanic languages, Baltic languages, and Slavic languages. This shows how cultures interacted. For example, many words for farming tools came from Germanic languages.
Importance of Finnic Languages
Finnic languages are important for several reasons. They are a key part of the culture in Finland and Estonia. They also help us understand human history.
Cultural Identity
For Finns and Estonians, their language is a big part of their identity. It connects them to their past. It also helps them share their unique stories and traditions. Learning these languages helps preserve their heritage.
Studying Language Evolution
Linguists study Finnic languages to learn about language change. They can see how languages evolve over time. This helps us understand how all languages work. It also shows how people migrated and interacted in ancient times.
See also
 In Spanish: Lenguas fino-bálticas para niños
In Spanish: Lenguas fino-bálticas para niños

