ScotRail facts for kids
| Rèile na h-Alba | |||
 |
|||

Two ScotRail Class 43 (HST) Inter7City trains at Pitlochry
|
|||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Franchise(s) | ScotRail | ||
| Main region(s) | Scotland | ||
| Other region(s) | North West England | ||
| Fleet size | |||
| Parent company | Scottish Rail Holdings | ||
| Headquarters | Glasgow | ||
| Reporting mark | SR | ||
| Dates of operation | 1 April 2022–present | ||
| Predecessor | Abellio ScotRail | ||
|
|||
ScotRail is a train company in Scotland. It is owned by the Scottish Government. ScotRail started running trains on April 1, 2022. It operates all the main train services across Scotland.
Contents
ScotRail's Story
Before April 2022, a private company called Abellio ScotRail ran the trains. In 2019, the Scottish Government's transport agency, Transport Scotland, decided that Abellio's contract would end. This was because the company had not met its performance goals.
In March 2021, Transport Scotland announced that a new private company would not take over. Instead, the Scottish Government would run the trains itself. This is called an "operator of last resort." Many train worker unions, like ASLEF and RMT, were happy about this change.
In February 2022, the Minister for Transport, Jenny Gilruth, confirmed that ScotRail would become publicly owned. She wanted to talk with people about how to make ScotRail better. She hoped for an affordable, green, and customer-focused train service.
Some politicians had different ideas. The Scottish Conservatives wanted lower fares and more services. The Scottish Liberal Democrats thought discussions about public ownership should have started earlier.
After ScotRail became publicly owned, some changes happened. On April 4, 2022, food and drinks started to be sold on trains again. This service had stopped during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In May 2022, some train drivers decided not to work extra hours. This led to many Sunday services being cancelled. ScotRail explained that the pandemic had made it hard to train enough new drivers. A temporary timetable was put in place on May 23, 2022. This meant about one-third fewer trains ran each day. Many early morning and late night trains were cancelled. By June 2022, the drivers' union suggested accepting a new pay offer.
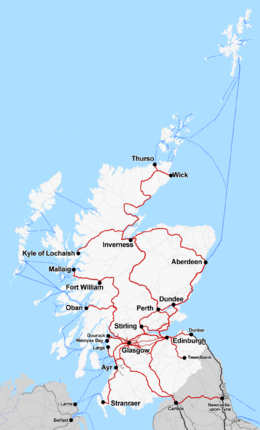
Train Routes
ScotRail runs many train services across Scotland. They connect big cities like Glasgow and Edinburgh with smaller towns and even remote areas.
As of May 2025, ScotRail operates trains in several key areas:
- Central Belt: This area includes busy routes around Glasgow and Edinburgh. Trains run on lines like the Argyle Line, North Clyde Line, and Cathcart Circle Lines.
- National Routes: ScotRail also runs longer journeys across Scotland. These include scenic routes like the West Highland Line to Oban and Mallaig. They also connect major cities like Glasgow and Edinburgh to Aberdeen and Inverness.
- Regional Lines: There are also services on lines like the Fife Circle Line, Borders Railway, and the Far North Line. These connect many communities throughout Scotland.
ScotRail's Trains
ScotRail uses different types of trains. Some run on diesel fuel, and others use electricity.
In 2021, ScotRail added special "Highland Explorer" carriages. These carriages are attached to some trains and have lots of space for bicycles. They also offer free refreshments and maps for cyclists.
ScotRail's fleet includes:
- Inter7City Trains: These are also known as Class 43 High Speed Trains. They are used for longer journeys between major cities like Glasgow, Edinburgh, Aberdeen, and Inverness.
- Sprinter Trains: These are diesel trains like Class 153, 156, and 158. They are used on many routes, including the West Highland Line and lines in the Glasgow South Western area.
- Turbostar Trains: These are Class 170 diesel trains. They operate on routes like the Fife Circle Line and the Borders Railway.
- Electric Trains: ScotRail uses several types of electric trains, including Class 318, 320, 334 (Juniper), 380 (Desiro), and 385 (Hitachi AT200). These trains run on electrified lines, especially around Glasgow and Edinburgh. The Class 385 trains are called "eXpress" and are used on many busy routes.
Making Trains Greener
Transport Scotland has a plan to make all domestic passenger train services carbon-free by 2035. This means replacing diesel trains with electric ones.
One part of this plan is to electrify 104 kilometers of the Fife Circle track. This work started in June 2022 and is expected to finish by December 2024. This will allow battery electric trains to run on these lines. More parts of the network will be electrified in the future.
Train Stations
As of March 2022, ScotRail operates 355 train stations in Scotland. Some big stations, like Edinburgh Waverley and Glasgow Central, are managed by Network Rail, not ScotRail. ScotRail also operates some stations where its trains don't currently stop, such as Lockerbie and Reston.
Train Maintenance Depots
ScotRail's trains are kept in good condition at several maintenance depots. These include locations like Edinburgh Haymarket, Glasgow Eastfield, Glasgow Shields Road, and Inverness. There are also newer depots built to help maintain the electric trains.
Images for kids