GNU GRUB facts for kids

The logo for GNU GRUB
|
|
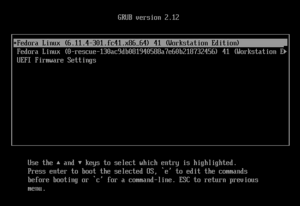
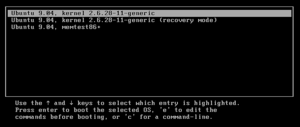
GRUB v2.12 running in text mode
|
|
| Original author(s) | Erich Boleyn |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | GNU Project |
| Initial release | 1995 |
| Stable release | |
| Preview release | |
| Written in | Assembly, C |
| Operating system | Linux, GNU/Hurd, macOS, BSD, (Solaris/ illumos (x86 port)), and Windows (through chainloading) |
| Platform | IA-32, x86-64, IA-64, ARM, PowerPC, Power ISA, s390x, MIPS, RISC-V, LoongArch and SPARC |
| Available in | English and others |
| Type | Bootloader |
| License | 2007: GPL-3.0-or-later 1999: GPL-2.0-or-later |
GNU GRUB (short for GNU GRand Unified Bootloader) is a special program that helps your computer start up. It's known as a boot loader, and it's part of the GNU Project, which creates free software.
Think of your computer's operating system (like Windows, macOS, or Linux) as the main driver of a car. Before the driver can take over, someone needs to start the engine. GRUB is like the key that starts the engine.
If you have more than one operating system on your computer (which is called multi-booting), GRUB shows you a menu when you turn it on. This menu lets you choose which operating system you want to use.
Contents
How GRUB Starts Your Computer
When you press the power button on your computer, a basic program called the BIOS or UEFI wakes up. Its job is to find the main hard drive and run the very first program it finds there. This first program is the boot loader.
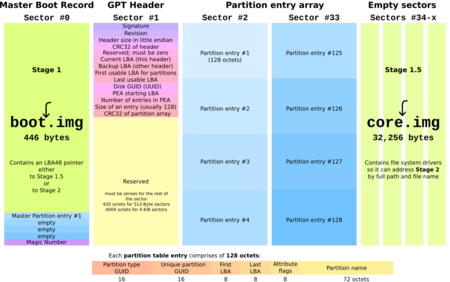
The space for this first program is tiny, so GRUB has to be clever. It splits itself into small pieces, or "stages."
The Old Way vs. The Smart Way
Early boot loaders needed a "map" that told them exactly where the operating system files were on the hard drive. If the files moved, the map became useless, and the computer wouldn't start. This was a big problem.
GRUB uses a smarter method. It understands how files are organized on the hard drive (the "file system"). This means GRUB can find the operating system by its name, no matter where it's located. This makes it much more reliable.
GRUB Legacy (Version 0)
This is the original version of GRUB, and it's not used much anymore. It worked in a few steps:
- Stage 1: A tiny piece of GRUB in the first part of the hard drive. Its only job was to load the next stage.
- Stage 1.5: This stage had the drivers to understand file systems. It would find and load the final stage.
- Stage 2: This was the main part of GRUB. It showed the menu and loaded the operating system you chose.
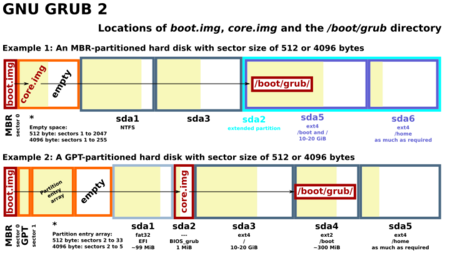
GRUB 2 (The Modern Version)
GRUB 2 is a complete rewrite and is much more powerful. It's the version used by most Linux systems today. How it starts depends on whether your computer uses the older BIOS or the newer UEFI system.
Starting with BIOS
- A tiny file called boot.img is placed in the first part of the hard drive.
- This loads a larger file called core.img, which is hidden in a small space near the beginning of the drive.
- core.img then loads the main menu and all the other parts it needs from a folder, usually located at
/boot/grub/.
Starting with UEFI
- UEFI systems are simpler. The computer's firmware directly loads a file called grubx64.efi from a special partition on the hard drive.
- This file then loads the GRUB menu, just like in the BIOS method.
Using the GRUB Menu
Once GRUB is running, it shows a menu listing the operating systems it found. You can use the arrow keys to pick one and press Enter.
GRUB also has some useful features for emergencies:
- By pressing the e key, you can edit the startup commands for an operating system. This is helpful if a bad driver is stopping your computer from booting. You can add a command to disable it.
- By pressing the c key, you can open the GRUB command line. This is a powerful tool for experts to fix boot problems manually.
History of GRUB
GRUB was first created by a programmer named Erich Boleyn. In 1999, it became an official part of the GNU Project. This meant that developers from all over the world could help improve it.
The original version is now called "GRUB Legacy." Developers then started working on a brand new version from scratch, called GRUB 2. The goal was to make it more powerful, modern, and able to work on more types of computers. GRUB 2 was officially released in 2012.
Today, most major Linux distributions, like Ubuntu, Fedora, and openSUSE, use GRUB 2 as their main boot loader.
Helpful Tools for GRUB
Because GRUB's configuration files can be complex, people have made tools to make it easier to manage.
- GRUB Customizer: A graphical tool that lets you change the order of the menu, set a background image, and change other settings without editing text files.
- Boot-Repair: A simple tool that can automatically fix common problems that stop your computer from booting. It can repair GRUB on many different Linux systems.
- Grub2Win: This is a program for Windows users. It lets you install and manage GRUB from within Windows, making it easy to set up a computer to boot both Windows and Linux.
See also
 In Spanish: GNU GRUB para niños
In Spanish: GNU GRUB para niños
- SysLinux – A bootloader often used for CDs and USB drives
- Windows Boot Manager – The bootloader used by modern versions of Windows
- rEFInd – Another boot loader for newer UEFI computers
- Comparison of bootloaders
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |