Software release life cycle facts for kids
The software release life cycle is like a journey a computer program takes from being an idea to something you can use. It's the whole process of creating, testing, and sharing a software product, like an operating system for your computer or phone.
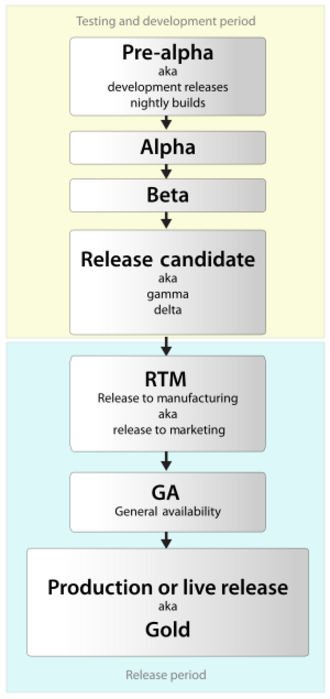
This journey usually has several steps. These steps include early stages like pre-alpha, alpha, and beta. Then come release candidates, which are almost ready. Finally, the "gold" or finished version is shared with everyone.
In the pre-alpha stage, the software is just being designed and built. Alpha testing is the first official testing. Here, the people who made the software test it themselves. Beta testing comes next. A larger group of users, often outside the company, tests the software. This beta stage focuses on making sure the software works well for users. It might also include checking how easy it is to use.
After beta testing, the software might have one or more release candidate stages. Here, it's made even better and tested more. Then, the final version is released.
Some software, especially on the internet, is always being updated. It's called "perpetual beta." This means it's never truly "finished." This way, new features can be added often. It also lets people start using the software sooner.
Contents
Steps in Software Development
What is Pre-alpha?
Pre-alpha includes everything that happens before official testing begins. This can involve figuring out what the software needs to do. It also includes designing it, writing the code, and testing small parts of it. For Open-source software, there can be different pre-alpha versions. These "milestone" versions are released when certain features are completed.
What is Alpha Testing?
The alpha phase is the first step of software testing. (Alpha is the first letter of the Greek alphabet). In this phase, developers usually test the software themselves. They use special methods to check the code. Then, another testing team might do more checks. This is called an alpha release when it's tested inside the company.
Alpha software is not fully tested before it's given to users. It might have serious errors. These errors could cause the program to crash or you could lose data. Alpha software might also not have all the features planned for the final version. Usually, you don't see alpha versions of paid software. But Free and open-source software often has public alpha versions. The alpha phase usually ends when no more new features will be added. At this point, the software is called feature-complete.
Is the Software Feature-Complete?
A feature-complete (FC) version of software has all its main features built. But it's not final yet. This is because it might still have bugs, or problems with software performance or stability. This stage happens at the end of alpha testing.
Usually, feature-complete software still needs more beta testing and bug fixing. It also needs improvements for speed or stability. After that, it can become a release candidate. Finally, it reaches gold status.
What is Beta Testing?
Beta, named after the second letter of the Greek alphabet, is the next step after alpha. The beta phase usually starts when the software has all its features. But it likely still has many known or unknown bugs. Software in beta often has more bugs than finished software. It might also have speed problems. It could still cause crashes or data loss. Beta testing focuses on making the software better for users. It often includes usability testing.
When a beta version is given to users, it's called a beta release. This is usually the first time the software is available outside the company that made it. Beta releases can be open or closed. This depends on whether they are available to everyone or only a small group. Beta software is often good for showing off new programs to potential customers. Some developers call this stage a preview or technical preview.
Beta testers are people who actively report problems with beta software. They are often customers or future customers. Beta testers usually volunteer their time. But they might get free versions of the product or discounts.
What is Perpetual Beta?
Some software stays in a perpetual beta state. This means new features are always being added. There's no single "stable" final release. The Internet has made it easy and cheap to share software quickly. Because of this, companies have started to use the word beta more loosely.
Open and Closed Beta Tests
Developers can release either a closed beta or an open beta. Closed beta versions are given to a small, invited group of people to test. Open beta testers come from a larger group, or anyone who is interested. A private beta might be good for software that works but isn't ready for everyone. This could be due to scaling issues or missing features. Testers report any bugs they find. Sometimes, they suggest new features for the final version.
Open betas help in two ways. They show the product to many possible users. Also, testing by a large group often finds hidden errors. A small testing team might miss these errors.
What is a Release Candidate?
A release candidate (RC) is like a beta version that could become the final product. It's ready to be released unless major bugs appear. At this stage, all features are designed, coded, and tested. This happens through one or more beta cycles. There are no known "showstopper" bugs (bugs that stop the program from working). A release is called code complete when the team agrees no new code will be added. There might still be small code changes to fix problems.
What is a Stable Release?
Also called a production release, the stable release is the last release candidate. It has passed all checks and tests. Any remaining known bugs are considered okay. This version is ready for people to use.
Some software, like certain Linux distributions, also have long-term support (LTS) releases. These are based on full releases that have been well-tested. They only receive security updates for a long time.
Releasing the Software
Once software is released, it's usually known as a "stable release." The exact name often depends on how it's shared. This could be on physical discs, online, or as a web application.
The released software usually gets an official name or version number.
What is Release to Manufacturing (RTM)?
The term "release to manufacturing" (RTM) means a software product is ready to be delivered. It's also known as "going gold." This version might have a digital signature. This lets you check that the software is real and hasn't been changed. The RTM version is called the "gold master" or GM. It's sent for mass copying onto discs if needed. This term comes from the music industry. RTM happens before general availability (GA), which is when the product is released to the public.
RTM is often used for software sold in stores, especially with computer hardware. It means the software is good enough for mass retail distribution. RTM can also mean the software has been given to a client for installation. The term doesn't say how it's delivered. It just means the quality is good enough for wide distribution.
What is General Availability (GA)?
General availability (GA) is the stage where all marketing steps are done. The software product is ready for people to buy. This depends on the language, region, and if it's online or on discs. Marketing steps can include security checks and making it available worldwide. The time between RTM and GA can be days to months. This is because all marketing activities need to be finished. At this stage, the software is "live."
What is Release to the Web (RTW)?
Release to the Web (RTW) or Web release is when software is delivered using the Internet. No physical discs are made by the company. Web releases have become very common as more people use the Internet.
Software Support
After software is released, it often gets updates. These are called service releases, patches, or service packs. They might also be called "interim releases" or "maintenance releases." For example, Windows XP received several service packs. These updates contain fixes and improvements. They might also add new features. Some software is released with the idea that it will get regular support. This includes things like Antivirus software and massively multiplayer online games.
What is End-of-Life?
When software is no longer sold or supported, it has reached its end-of-life. It might be called discontinued, retired, or obsolete. But people might still use it for some time, even if it's very old.
After the end-of-life date, the developer usually won't add new features. They also won't fix existing problems or provide any support. If the developer wants, they might release the software's source code. This lets volunteers keep it updated.
How Software Testing Started
The terms "alpha" and "beta" testing started at IBM. Similar words were used at IBM from at least the 1950s. An "A" test was checking a new product before telling the public about it. A "B" test was checking it before it was made in large numbers. A "C" test was the final check before it was available to everyone. As software became important for IBM, "alpha test" meant the pre-announcement test. "Beta test" meant it was ready for general use. Martin Belsky, a manager at IBM, said he invented the terms. IBM stopped using "alpha/beta" in the 1960s. But by then, the terms were widely known. IBM used "field test" for testing done by customers, not "beta test."
Later, major public beta tests happened. Early customers bought a "pioneer edition" of the WordVision word processor for the IBM PC. In 1984, Stephen Manes wrote that the company got people to pay to test the product. In September 2000, Apple released a boxed version of its Mac OS X Public Beta operating system. Between September 2005 and May 2006, Microsoft released "community technology previews" (CTPs) for Windows Vista. From 2009 to 2011, Minecraft was in public beta.
In February 2005, ZDNet wrote about beta versions staying for years. They were used as if they were finished products. For example, Gmail and Google News were in beta for a long time, even though many people used them. Google News left beta in January 2006. Google Apps (now Google Workspace), including Gmail, left beta in July 2009. Since Windows 8, Microsoft has called pre-release software a preview instead of beta. All pre-release versions released through the Windows Insider Program since 2014 are called "Insider Preview builds." "Beta" can also mean something like a release candidate. Or it can be a limited-time demo or a marketing tool.
See also
 In Spanish: Ciclo de vida del lanzamiento de software para niños
In Spanish: Ciclo de vida del lanzamiento de software para niños
- Application lifecycle management
- Application-release automation
- Application retirement
- Release engineering
- Release management
- Rolling release
- Software deployment
- Software versioning