Genetic disorder facts for kids
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by changes in a person's genome, which is like their body's instruction manual. These changes are often inherited from parents and can be passed down through genes. If a genetic disorder is present when a baby is born, it's called a congenital defect. Some genetic disorders might not show up until later in life.
Contents
What are Genetic Disorders?
Most genetic disorders are quite rare. They might affect only one person out of thousands or even millions. However, some are more common in certain groups of people. For example, some recessive gene disorders can give a special advantage in certain environments if a person only has one copy of the changed gene. Sickle cell anaemia is a good example of this.
Inherited vs. Non-inherited Conditions
Sometimes, the same health problem, like certain types of cancer, can be caused in different ways. It might be due to an inherited genetic change in some people. In others, it could be from new changes in their genes that weren't inherited. Or it could be caused by things that are not genetic at all. A health problem is only called a genetic disorder if it is inherited from parents.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
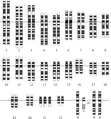
Chromosomes in Down syndrome, a common human condition. There are three chromosomes 21 (in the last row) instead of two.
-
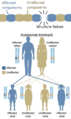
When a problem is caused by a faulty enzyme, it's usually inherited in a recessive way. This means you need two copies of the faulty gene (one from each parent) to show symptoms. If you only have one copy, the working enzyme from the good gene is usually enough to keep you healthy.
-
On the other hand, problems with structural proteins (like in osteogenesis imperfecta or Marfan's syndrome) are often inherited in a dominant way. This means just one faulty gene copy can cause the problem. The faulty protein can make the whole structure not work properly.
See also
 In Spanish: Enfermedad genética para niños
In Spanish: Enfermedad genética para niños