Genetic variation facts for kids
Genetic variation means the differences in DNA among living things, or the differences between groups of the same type of living thing. These differences are super important because they help species adapt and survive over time. The main ways these differences happen are through mutation (changes in DNA) and genetic recombination (when DNA mixes up). While mutations are the original source of new variations, other things like genetic drift (random changes in gene frequency) also play a part.
Contents
How We See Genetic Differences in Living Things
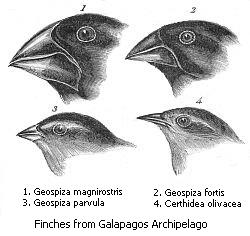
We can spot genetic variation in many ways. Sometimes, you can see it just by looking at how living things appear. For example, dogs have different leg lengths, or certain flowers have petals that are white, pink, or red. These are called phenotypic variations.
Scientists can also find genetic differences by looking at tiny parts of cells, like enzymes. They use a process called protein electrophoresis to see if genes have more than one version (called an allele). For example, about half of the genes that make enzymes in insects and plants can have many different versions!
The real reason for genetic variation comes down to the order of building blocks (called nucleotides) in genes. Thanks to new technology, scientists can now directly read DNA. This has shown even more genetic differences than we knew about before. They've found variations in parts of genes that code for proteins and even in parts that don't.
If a change in the DNA sequence leads to a different order of amino acids in a protein, and that difference changes how the protein works, then you'll see a physical difference in the living thing.
Differences Between Groups of Living Things
When groups of living things are separated by geography, they can develop differences over time. This is called geographic variation. Things like natural selection (where certain traits help survival), genetic drift (random changes), and gene flow (when genes move between groups) all help create these differences.
How We Measure Genetic Variation
Scientists often measure genetic variation within a group by looking at how many gene locations have more than one version (polymorphic loci) or how many individuals have two different versions of a gene (heterozygous). This helps them understand how living things adapt to their environment.
Where Genetic Variation Comes From
The main source of all genetic variation is random mutations. Mutations are changes in the DNA. Most mutations are either harmless or even bad, but sometimes a new mutation can be helpful and favored by natural selection. For example, polyploidy is a type of mutation where an organism ends up with three or more full sets of chromosomes instead of the usual two.
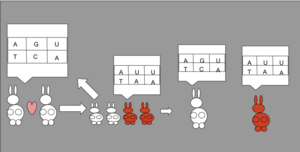
Another big source of variation is genetic recombination, which happens during meiosis (the process of making reproductive cells). During meiosis, DNA can swap pieces (crossing over) and chromosomes can sort themselves randomly. This creates new combinations of alleles. Also, when an egg and sperm combine, it's a random process, which adds even more variation.
Different Kinds of Genetic Variation
Genetic variation can show up in different ways, depending on the size and type of change in the DNA:
- Small changes: These are tiny differences, like a single base-pair substitution (one DNA building block swapped for another) or indels (small pieces of DNA added or removed).
- Big changes: These are larger differences in the structure of chromosomes. They can include copy number variation (when a section of DNA is copied too many times or is missing), or chromosomal rearrangements (like when parts of chromosomes move to a different spot or flip around).
- Whole chromosome changes: Sometimes, there can be an extra or missing whole chromosome, or even extra sets of all chromosomes (like in polyploidy).
Keeping Genetic Variation Alive in Groups
Many things help keep genetic variation present in populations. For example, if a harmful gene is recessive, it might be hidden in individuals who also have a normal, dominant gene. This way, the harmful gene can stay in the population without causing problems unless an individual gets two copies of it. Natural selection can also help maintain variation, especially when having two different versions of a gene is actually better than having two of the same.
Genetic Variation in RNA Viruses
RNA viruses, like the flu virus or HIV, have a lot of genetic variation. This is partly because they don't have a "proofreading" system for their genetic material, so they make many mistakes (mutations) when they copy themselves. These mutations help them change quickly and adapt. Genetic recombination also plays a big role for RNA viruses. If two different RNA viruses infect the same cell, they can swap genetic material, creating new combinations. This helps viruses like poliovirus and SARS evolve. This ability to recombine also helps them deal with damage to their genetic material. Sometimes, different types of animal viruses can recombine, and the new virus might then cause outbreaks in humans.
See also
 In Spanish: Variación genética para niños
In Spanish: Variación genética para niños
- Genetic diversity
- Genetic variability
- Human genetic variation