Glial cell facts for kids
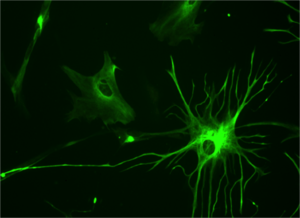
Glial cells are tiny but super important cells in your nervous system. Think of them as the helpful support crew for your brain and nerves! The word "glia" comes from Greek and means "glue," which is a great way to describe them because they help hold everything together. You can find glial cells in both the grey matter and white matter parts of your brain.
Glial cells have several key jobs:
- They surround and hold neurons (your main brain cells) right where they need to be.
- They deliver important nutrients and oxygen to neurons, keeping them healthy.
- They act like insulation, making sure signals from one neuron don't get mixed up with others.
- They clean up! They destroy harmful pathogens (like germs) and remove dead neurons, keeping your brain tidy.
Scientists are always discovering new things about glial cells, so they might have even more cool jobs than we know about right now!
Glial Cells and Brain Health
Some types of glial cells are thought to be involved in certain brain conditions. For example, a type of glial cell called microglia acts like the "clean-up crew" or macrophages of the nervous system.
In some brain diseases, like Alzheimer's disease (which affects memory), Parkinson's disease (which affects movement), and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS, which affects muscle control), microglia might sometimes cause problems. Instead of just cleaning up bad cells, they might accidentally start to damage healthy brain cells.
For instance, in Parkinson's disease, microglia are thought to break down special cells that produce dopamine, a chemical important for movement. This can lead to the symptoms seen in Parkinson's. Scientists are studying these cells to understand how they can help, not harm, the brain.
Images for kids
-
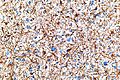
Cancerous glial cells from a brain biopsy, stained brown to show GFAP.
See also
 In Spanish: Célula glial para niños
In Spanish: Célula glial para niños