Gram-negative facts for kids
Gram-negative bacteria are a type of bacteria. They are special because of how their cell walls are built. This difference is important for how scientists identify them and how we treat infections they cause.
Scientists use a test called the Gram stain to tell bacteria apart. In this test, Gram-negative bacteria do not hold onto a purple dye called crystal violet. Instead, they turn red or pink when a second dye, safranin, is added.
Contents
What is the Gram Stain Test?
The Gram stain test helps scientists sort bacteria into two main groups: Gram-positive and Gram-negative. This test was invented by a Danish scientist named Hans Christian Gram in 1884. It's a very useful tool in microbiology.
Here's how the test works:
- First, bacteria are stained with crystal violet, which is purple.
- Then, a special solution is added to help the dye stick.
- Next, a decolourizing solution is used. This is where the difference shows up!
- Finally, a red or pink counterstain (safranin) is added.
Gram-negative bacteria don't keep the purple dye when the decolourizing solution is used. This is because they have a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane. This outer membrane acts like a shield, stopping the purple dye from staying inside. So, when the red dye is added, they turn pink or red.
Why Gram-Negative Bacteria are Different
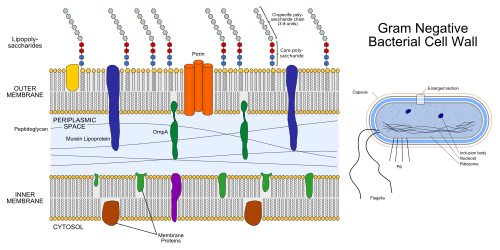
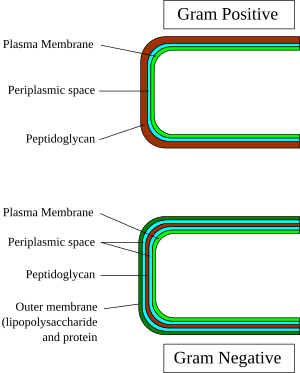
The main difference between Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria is their cell wall structure. Gram-negative bacteria have a more complex cell wall. It includes:
- A thin layer of peptidoglycan (a mesh-like material).
- An outer membrane that surrounds the peptidoglycan layer.
This outer membrane is made of fats and sugars, including something called lipopolysaccharide (LPS). This special outer layer makes Gram-negative bacteria tougher. It helps them resist certain chemicals and even some antibiotics.
Gram-Negative Bacteria and Your Body
The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, especially the LPS part, can affect humans. When these bacteria are in your body, the LPS can trigger your immune system. This is your body's natural defense system.
When your immune system detects LPS, it sends out signals called cytokines. These signals help fight off the bacteria. Sometimes, this can lead to inflammation, which is when a part of your body becomes red, swollen, and warm. It's your body's way of trying to heal itself.
Fighting Gram-Negative Infections
Because of their strong outer membrane, Gram-negative bacteria can be harder to treat with antibiotics than Gram-positive bacteria. The outer membrane acts like a barrier, making it difficult for some medicines to get inside the bacterial cell and kill it.
Scientists are always working to find new ways to fight these tough bacteria. Understanding their unique cell wall helps doctors choose the right antibiotics to treat infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria.
Images for kids
-
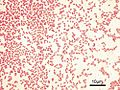
Microscopic image of gram-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria (pink-red rods)
See also
 In Spanish: Bacteria gramnegativa para niños
In Spanish: Bacteria gramnegativa para niños
 | DeHart Hubbard |
 | Wilma Rudolph |
 | Jesse Owens |
 | Jackie Joyner-Kersee |
 | Major Taylor |