Gram staining facts for kids
Gram staining is a special way to sort bacteria into two main groups: gram-positive and gram-negative. It's also called Gram's method. This method helps scientists tell different bacteria apart.
The technique was invented by a scientist named Hans Christian Gram. He created it in 1884.
Contents
How Gram Staining Works
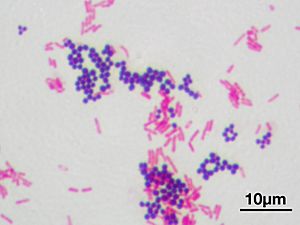
Gram's method uses special dyes to color bacteria. Bacteria have different types of cell walls. These walls react differently to the dyes.
- First, a purple dye is added to the bacteria. This dye sticks to a thick layer called peptidoglycan. This layer is found only in gram-positive bacteria. So, gram-positive bacteria turn purple.
- Next, another dye, usually red or pink, is added. This dye colors the bacteria that did not turn purple. These are the gram-negative bacteria. They end up looking red or pink.
So, after Gram staining, you can see two colors of bacteria. Purple bacteria are gram-positive. Red or pink bacteria are gram-negative.
Why Gram Staining Is Important
Gram staining is often the first step in finding out what kind of bacteria is causing a problem. For example, if someone is sick, doctors can use this test. It helps them choose the right medicine to fight the infection.
However, not all bacteria can be sorted this way. Some bacteria are called 'gram-variable' or 'gram-indeterminate'. This means the Gram stain does not work well for them.
History of Gram's Method
Hans Christian Gram developed this technique while working in a hospital in Berlin. He was working with another scientist, Carl Friedländer.
Gram first used his test to make bacteria in the lungs easier to see. He published his complete method in 1884. This made it possible for other scientists to use his helpful discovery.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Tinción de Gram para niños
In Spanish: Tinción de Gram para niños