Guayrá facts for kids
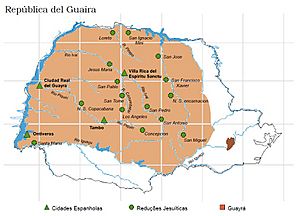
Guayrá was an important historical region during the time of the Spanish Empire. It was part of the Governorate of Paraguay and the larger Viceroyalty of Peru. Today, this area is found in parts of Paraguay and the state of Paraná in Brazil.
The name Guayrá has a few possible meanings. Some say it came from a local leader, a cacique, named Guayrá or Guayracá. Others believe it comes from the Guarani language. It might mean "cannot pass" or "impassable." Another idea is "river that goes beyond."
Contents
Where Was Guayrá Located?
The Guayrá region had clear natural borders. To the south, it was bordered by the Iguazu River. The Paraná River formed its western edge. In the north, the Tiete River (also called Añemby) marked the boundary. The eastern border followed the line set by the Treaty of Tordesillas. The Tiete River also separated the lands of the Tupi and Guarani tribes.
Key Events in Guayrá's History
The history of Guayrá includes the founding of early towns. It also saw the arrival of different groups of people.
Early Spanish Settlements
In 1554, the town of Ontiveros was founded. Captain Garcia Rodriguez de Vergara started it. This was done under orders from Domingo Martínez de Irala. Ontiveros was located on the left bank of the Paraná River. It was meant to connect Spanish lands with Portuguese Colonial Brazil.
Two years later, in 1556, Ciudad Real del Guayrá was founded. This town is also known as Guayrá. Today, it is called Guaíra, Paraná. Captain Ruy Diaz Melgarejo founded this settlement. It was also on the left bank of the Paraná River.
A Place of Refuge
By the year 1600, Guayrá was a dense forest region. It had many rivers. This made it a safe place for the Guarani people. They sought refuge there from the encomenderos of Paraguay. Encomenderos were Spanish settlers who forced indigenous people to work for them. The Guarani also hid from the Bandeirantes from Brazil. These Bandeirantes were explorers and slave hunters.
Early Explorers in Guayrá
Some of the first European explorers passed through Guayrá. Aleixo Garcia crossed the region in 1522. Later, in 1542, Alvar Nunez Cabeza de Vaca traveled through the southern parts of Guayrá. He was on his way to Asunción from Santa Catarina Island.
The Jesuit Missions of the Guaranis
Guayrá became a very important area for the Spanish Jesuit reductions. These were special communities. Here, Jesuit priests gathered indigenous people, mainly the Guarani. They taught them about Christianity and European ways of life. These missions were part of the larger Jesuit Missions of the Guaranis.
However, these missions faced a big threat. In 1631, bandeirantes from São Paulo attacked the region. They destroyed many of the Jesuit missions in Guayrá. This forced the Guarani and the Jesuits to move to safer areas.
See also
- Guarani people
- Governorate of Paraguay
- Spanish Jesuit Missions of the Guaranis−related topics — World Heritage Sites
- Governorate of the Río de la Plata
- Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata
 In Spanish: Guayrá para niños
In Spanish: Guayrá para niños
 | William Lucy |
 | Charles Hayes |
 | Cleveland Robinson |

