Gynoecium facts for kids

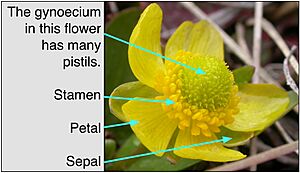

The gynoecium (say: guy-NEE-see-um) is the female part of a flower. It comes from an old Greek word meaning "woman." This is where a flower makes its seeds. The male parts of a flower are called the androecium. Some flowers have both male and female parts, while others only have one or the other.
Inside the gynoecium, you'll find one or more pistils. A pistil is made up of smaller units called carpels. A pistil can have just one carpel, or several carpels joined together.
Each carpel or pistil has three main parts:
- The stigma is at the very top. This is the sticky part where pollen lands.
- The style is a stalk-like part. It connects the stigma to the ovary.
- The ovary is at the bottom. It holds the tiny ovules, which can grow into seeds.
Sometimes, the stigma, style, and ovary of a pistil are made from parts of many carpels that have grown together. The plant's ovary is similar to an animal's ovary because it holds the ovules. The style is usually a thin stalk between the ovary and the stigma. Some plants have pistils without a style. The stigma is the part that receives pollen. Stigmas can be separate or form a special "stigmatic region."
Contents
Parts of a Carpel
A carpel is the basic unit of a flower's female reproductive system (the gynoecium). Here are its parts:
- The stigma: This is the top part that receives pollen. It is often sticky to help pollen stick to it.
- The style: This is a stalk that connects the stigma to the ovary. It has a special path that helps the pollen tube grow. This tube carries the male cell to the ovule.
- The ovary: This part holds the female reproductive cells, called ovules.
The Ovule and Seed Production
The ovule is like a tiny egg inside the ovary. When it is ready, it has one or two protective layers around its central part, called the nucellus. There is a small opening at the top called the micropyle. The nucellus is a tissue that surrounds one large cell, called the megaspore. This large cell divides to create the egg cell and other cells needed for reproduction.
A good example of a simple carpel is found in a pea, bean, or Arabidopsis plant. The fruit of these plants grows from a single carpel. It has two rows of ovules lined up along a special edge called the placental margin.
Understanding the Pistil
The term pistil is another way to describe the female parts of a flower. This table helps explain how it's used:
| What the Gynoecium is Made Of | Carpel Term | Pistil Term | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Just one carpel | Monocarpous (meaning "one carpel") gynoecium | A simple pistil | Avocado (Persea species), most legumes (like peas and beans) |
| Many separate carpels (not joined) | Apocarpous (meaning "separate carpels") gynoecium | Simple pistils (many of them) | Strawberry (Fragaria species), Buttercup (Ranunculus species) |
| Many carpels joined together ("fused") | Syncarpous (meaning "joined carpels") gynoecium | A compound pistil | Tulip (Tulipa species), most flowers you see |
Images for kids
-
A cut-through view of the ovary of Narcissus showing many joined carpels (a compound pistil). The ovules form along the placental line in each section.
-
Longitudinal section of a female flower of squash showing the ovary, ovules, stigma, style, and petals
-
Stigma of a Crocus flower.
See also
 In Spanish: Gineceo para niños
In Spanish: Gineceo para niños












