Haiku (operating system) facts for kids
 |
|
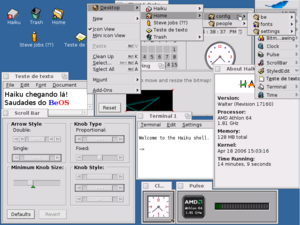
Screenshot of Haiku (Beta 3)
|
|
| Company / developer | Community contributors and Haiku, Inc. |
|---|---|
| Programmed in | C, C++ |
| OS family | BeOS, Unix-like |
| Working state | Beta |
| Source model | Open source |
| Initial release | February 15, 2002 |
| Latest unstable release | R1 Beta 5 / September 13, 2024 |
| Available language(s) | Multilingual |
| Package manager | hpkg |
| Supported platforms | IA-32, x86-64, RISC-V |
| Kernel type | Hybrid |
| Default user interface | OpenTracker |
| License | MIT License and Be Sample Code License |
Haiku, first called OpenBeOS, is a free and open-source operating system for personal computers. It's like a new version of an older system called BeOS. People from all over the world work together to build it. Haiku tries to work with old BeOS programs. The Haiku project started in 2001. A group called Haiku Inc. helps support it. The operating system is still in a testing phase, known as "beta."
Contents
What is Haiku?
Haiku is a computer operating system, just like Windows or macOS. It's special because it's "open-source." This means its code is free for anyone to see, use, and change. Many people work together to make Haiku better.
How Haiku Started
In 2001, a company bought Be, Inc., which made the BeOS system. This meant BeOS would no longer be updated. A person named Michael Phipps then started the OpenBeOS project. His goal was to create a new, open-source system that worked like BeOS.
Since they couldn't use the old BeOS code, they had to build Haiku from scratch. In 2003, Phipps started Haiku, Inc. This group helps get money to support the project.
Renaming the Project
In 2004, the project changed its name from OpenBeOS to Haiku. This was done to avoid problems with trademarks. The name "Haiku" comes from a type of Japanese poem. It also refers to the short, clear messages that BeOS programs used.
People who worked on BeOS, including its creator Jean-Louis Gassée, have shown support for Haiku. There's even an annual meeting in Germany called BeGeistert. It has been held since 1998, even when BeOS was still active.
How Haiku is Built
Haiku is mostly new software, except for some parts like its file manager (Tracker) and taskbar (Deskbar). These parts were made open-source by BeOS. Haiku's design is very organized. Different teams could work on separate parts of the system at the same time.
Early Steps in Development
One of the first things the OpenBeOS project did was create an update for BeOS 5.0.3 in 2002. This update included new open-source versions of some BeOS parts. Haiku's core, called the kernel, was based on a project called NewOS. This happened in 2002.
In 2005, the part of Haiku that handles windows and graphics was finished. A developer named Stephan Aßmus created Icon-O-Matic in 2006. This is a tool for making icons. He also made a special way to store icons called HVIF.
Adding New Features
Over time, Haiku gained support for Java programs. It also got WLAN (wireless internet) support from another system called FreeBSD. After many years of work, the first test version, called "alpha," was released in 2009.
At first, Haiku aimed to be exactly like BeOS 5. But then, the community decided to make it more modern. They wanted it to work with new computers, internet tools, and other free software. In 2009, Haiku also got support for Qt4, which helps create user interfaces.
The WebPositive browser was included in a later alpha release. It replaced an older browser. A lot of effort then went into creating a system for managing software packages. This system started working in 2013.
The first "beta" release of Haiku came out in 2018. This version was important because it included a full package management system. This system lets users easily install and update software. The latest beta version, R1 Beta 5, was released in September 2024.
Haiku Release History
| Version | Release date | OS name | Architecture | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haiku R1/Alpha1 | 2009-09-14 | hrev33109 | IA-32 | |
| Haiku R1/Alpha2 | 2010-05-10 | hrev36769 | ||
| Haiku R1/Alpha3 | 2011-06-20 | hrev42211 | ||
| Haiku R1/Alpha4 | 2012-11-11 | hrev44702 | IA-32, X86-64 | |
| Haiku R1/Beta1 | 2018-09-28 | hrev52295 | ||
| Haiku R1/Beta2 | 2020-06-09 | hrev54154 | ||
| Haiku R1/Beta3 | 2021-07-26 | hrev55182 | ||
| Haiku R1/Beta4 | 2022-12-23 | hrev56578 | ||
| Haiku R1/Beta5 | 2024-09-13 | hrev57937 | ||
|
Legend:
Old version
Latest preview version
|
||||
Haiku's Design
Haiku is written in a computer language called C++. It uses an object-oriented way of building programs. This makes it easier to organize the code. Haiku's kernel, the core of the system, is a mix of different types of kernels. It started from NewOS, another modular kernel.
Haiku can run on 32-bit and 64-bit x86 computers. It has also been made to work on RISC-V processors. There is also work being done to make it run on ARM devices.
How Programs Talk to Haiku
Haiku has an API, which is like a set of rules for programs to follow. This API is based on the one from BeOS. It's divided into "kits" that group similar tools together. In 2007, the company that owned BeOS's information made the BeOS API guide free to use.
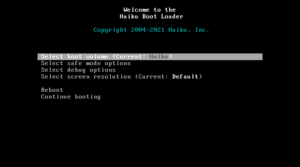
Haiku's boot loader helps start the system. It can also start other boot loaders like GRUB or LILO. Since the Beta1 release, Haiku has features to make it more secure. These features help protect the computer's memory.
Graphics and windows are managed by a part called `app_server`. If special graphics drivers aren't available, Haiku can use a basic video mode. Haiku also works with POSIX standards. This means it can run many programs made for other Unix-like systems.
User Interface
Haiku's look and feel are made up of two main parts. One is Tracker, which is like a file explorer. The other is the Deskbar, which is a taskbar always on top of the screen. The Deskbar has a menu, a system tray, and a list of programs that are running.
Tracker is an improved version of OpenTracker. The icons in Haiku are called stippi and were designed by Stephan Aßmus. He also created a special way to store these icons called HVIF. This format helps icons look good and load quickly.
Software on Haiku
Haiku has a system for managing software called HaikuDepot. It's a graphical app that lets you easily find and install programs. There's also a command-line tool called `pkgman` that does the same thing. You can get software from online stores or by dropping files into a special folder.
Haiku comes with several programs already installed. These include:
- WebPositive: A web browser for surfing the internet.
- BePDF: A program for reading PDF documents.
- PoorMan: A simple web server.
- Pe and StyledEdit: Text editors for writing.
- Vision: A chat program for IRC.
- Terminal: A program for typing commands.
Working with BeOS Programs
Haiku R1 is designed to work with programs made for BeOS 5. This means that software written for BeOS can often run on Haiku without changes. However, the 64-bit version of Haiku doesn't work with old BeOS programs directly. But the way programs talk to the system (the API) is still compatible.
See also
 In Spanish: Haiku (sistema operativo) para niños
In Spanish: Haiku (sistema operativo) para niños
- Comparison of operating systems
- List of BeOS applications
- Syllable Desktop
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |