Haemolymph facts for kids
Haemolymph is a special fluid, a bit like blood, found in insects, spiders, crabs, and other creatures called arthropods. Even some molluscs, like snails, have a similar system. Unlike human blood, haemolymph does not carry oxygen using hemoglobin.
Contents
What is Haemolymph?
Haemolymph is a fluid that fills the body cavity of many invertebrates. It acts like blood, carrying nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body. However, it works differently from the blood in humans and other vertebrates.
Haemocyanin: The Oxygen Carrier
Instead of haemoglobin, insects and their relatives use a molecule called haemocyanin. This molecule does a similar job to haemoglobin, but it uses copper instead of iron to carry oxygen. Because of the copper, haemocyanin often gives the haemolymph a bluish or greenish color when it's carrying oxygen, not red like human blood.
How Haemolymph Moves Around
Insects and arthropods have what's called an open circulatory system. This means their haemolymph doesn't stay inside blood vessels like veins or arteries. Instead, it moves freely through a large space inside their body called the haemocoel.
The Haemocoel and Organs
Imagine a bathtub filled with water; the organs of an insect are like sponges floating in that tub. The haemocoel is this open space where the organs sit directly in the haemolymph. The fluid bathes the organs, delivering what they need and picking up waste.
The Simple Heart
Insects do have a "heart," but it's much simpler than a human heart. It's usually a long, tube-like structure that runs along the back of the insect. This tube pulses or squeezes, pushing the haemolymph forward. The haemolymph then flows out into the haemocoel, surrounds the organs, and eventually makes its way back to the heart through small openings called ostia. This simple pumping action keeps the haemolymph circulating throughout the insect's body.
Images for kids
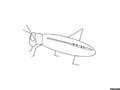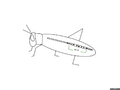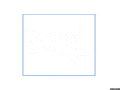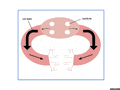
-
Above is a diagram of an open circulatory system. An open circulatory system is made up of a heart, vessels, and hemolymph. This diagram shows how the hemolymph is circulated throughout the body of a grasshopper. The hemolymph is first pumped through the heart, into the aorta, dispersed into the head and throughout the hemocoel, then back through the ostia that are located in the heart, where the process is repeated.