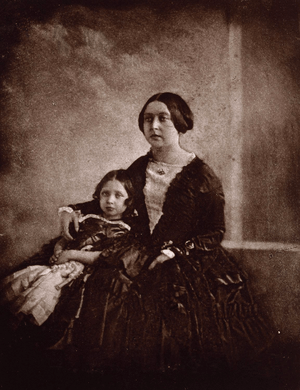Henry Collen facts for kids
Henry Collen (born October 9, 1797, in Middlesex – died May 8, 1879, in Brighton) was an English artist. He was a special portrait painter for Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom and her mother, the Duchess of Kent. Later, he became a pioneer in photography. He was the first professional photographer in London to use a new method called the calotype. Collen combined his artistic skills with this exciting new technology.

Contents
Early Life and Art Training
Collen was born in Middlesex, England. He studied painting at the Royal Academy of Arts. This was a famous art school in London. He learned from Sir George Hayter, who was a well-known artist. The Hayter family remained good friends with Collen for many years.
Painting for Royalty
Henry Collen knew Princess Victoria very well. She later became Queen Victoria. He was her drawing teacher and painted tiny portraits of her. These small paintings are called miniatures. In 1833, for her 14th birthday, he gave her a special painting for her album. She often sat for him to paint her picture.
Collen was a very active artist. Between 1820 and 1872, he showed more than 100 paintings. He displayed them at the Royal Academy and the Society of Botanical Artists. In 1821, he won a silver medal at the Royal Academy. This was a great achievement for him.
Becoming a Photographer
In the 1840s, Collen became very interested in photography. He especially liked the calotype process. This was a new way to make photos using paper negatives. His friend, Henry Fox Talbot, invented this process. Collen used his art skills with Talbot's photography knowledge. He created unique photos that he often painted over.
In August 1841, Talbot gave Collen a special license. This made Collen the first professional calotype photographer in London. He opened his own studio at 29 Somerset Street. There, he took about 1,000 portraits. People praised his work for its high quality.
Collen is believed to have taken the first known photograph of Queen Victoria. This picture was taken around 1844 or 1845. His photographic miniatures mixed traditional painting with new photography. He often added paint to make them even better.
Important Projects
Collen also worked with Francis Ronalds. Ronalds was in charge of the Kew Observatory. They worked together to create machines that used photography. These machines helped record weather information.
In 1842, Collen got a special job. He was asked to make photographic copies of the Treaty of Nanking. This treaty ended the Opium Wars. This project is seen as one of the first times an official document was "photocopied."
Later Life
Henry Collen continued to paint and take pictures of important people. He worked until he passed away on May 8, 1879. He died in Brighton, England. His work is a very important part of early photography history.
Family Life
On August 12, 1826, Henry Collen married Ellen Dison. She was born in 1805. They had one son together, named Edwin Henry Hayter Collen.