Hip facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Hip |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Bones of the hip region | |
| Latin | coxa |
The hip is a very important part of your body. It's found where your leg connects to your main body. In science, the hip can mean two things: a specific area of your body, or the actual joint that lets your leg move. Doctors sometimes call the hip "coxa".
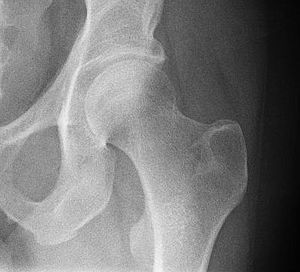
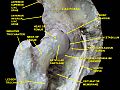
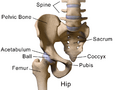
The hip region is the side and front part of your body, just below your waist. It's above the big bone you can feel at the top of your pelvis, called the iliac crest. This area also covers the top part of your femur, which is your thigh bone. In adults, three bones of the pelvis join together to form the hip bone. This hip bone includes the acetabulum, which is a cup-shaped part.
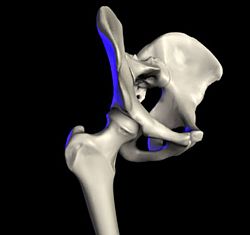
The hip joint is the amazing connection between your femur (thigh bone) and the acetabulum of your pelvis. Its main job is to hold up your body's weight. It does this when you are standing still or moving around. For example, it helps you walk, run, and keep your balance. This joint is super important for staying upright and keeping your pelvis in the right position.
Sometimes, people can feel pain in their hip. This pain can happen for many reasons. It might be due to nerves, osteoarthritis (wear and tear), infections, injuries, or even things you are born with.
How Your Hip is Built
The Hip Region
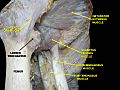
The top part of your thigh bone, the femur, is mostly covered by muscles. Because of this, the greater trochanter is often the only bone you can feel in your hip area. It's a bumpy part on the side of your upper thigh.
The Hip Joint
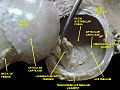
The hip joint is a special type of joint called a synovial joint. It's formed where the round head of your femur (thigh bone) fits into the cup-shaped acetabulum of your pelvis. Think of it like a ball and socket! This joint is the main link between your leg bones and the central part of your body, which includes your spine and pelvis. Both surfaces of the joint are covered with a smooth, slippery layer. This layer is called articular hyaline cartilage, and it helps the bones glide easily.
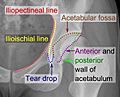
The cup-shaped acetabulum is made from three different bones of your pelvis. These are the ilium, the pubis, and the ischium. There's a Y-shaped growth plate that separates these bones when you are young. It's called the triradiate cartilage. This plate fully fuses together when you are about 14 to 16 years old.
The hip joint is a type of ball and socket joint. The round head of the femur fits deeply into the acetabulum. The femoral head is about 2.5 centimeters (1 inch) wide. The acetabulum holds almost half of the femoral head. A ring of tough tissue, called the acetabular labrum, makes this grip even stronger. It extends the joint even further around the ball. The space between the femoral head and the top of the acetabulum is usually between 2 and 7 millimeters wide.
The head of the femur is connected to the main shaft of the bone by a thinner neck area. This neck can sometimes break, especially in older people. This often happens because of a condition called osteoporosis, which makes bones weaker.
Images for kids