United States Department of Homeland Security facts for kids

|
|

Flag of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security
|
|
 Headquarters of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security in Washington D.C. |
|
| Agency overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed | November 25, 2002 |
| Jurisdiction | U.S. federal government |
| Headquarters | St. Elizabeths West Campus, Washington, D.C., U.S. 38°51′17″N 77°00′00″W / 38.8547°N 77.0000°W |
| Employees | 240,000 (2018) |
| Annual budget | $103.2 billion (FY 2024) |
| Agency executives |
|
| Child agency |
|
| Key document |
|
| Agency ID | 7000 |
|
"The DHS March" |
|
The United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) is a big part of the U.S. government. Its main job is to keep the country safe. Think of it like a national safety team. It works to protect the United States from dangers both inside and outside its borders.
DHS handles many important tasks. These include stopping terrorism, keeping borders secure, and managing immigration. They also work on cybersecurity, which means protecting computer systems from attacks. Other jobs involve keeping transportation safe, like at airports, and helping with sea rescues. They also work to prevent dangerous weapons from being used.
DHS started its work on March 1, 2003. It was created after the September 11 attacks in 2001. These attacks showed the need for a single department to focus on homeland security. With over 240,000 employees, DHS is one of the largest government departments. Only the departments of Defense and Veterans Affairs are bigger.
Contents
- History of DHS
- What DHS Does
- How DHS is Organized
- Key Agencies within DHS
- U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services
- U.S. Coast Guard
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection
- U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency
- U.S. Federal Emergency Management Agency
- U.S. Federal Law Enforcement Training Centers
- U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement
- U.S. Secret Service
- U.S. Transportation Security Administration
- DHS Management Directorate
- DHS Science and Technology Directorate
- DHS Countering Weapons of Mass Destruction Office
- DHS Office of Intelligence and Analysis
- DHS Office of Homeland Security Situational Awareness
- DHS Office of Health Security
- DHS Office of Inspector General
- DHS Office of the Secretary
- Key Agencies within DHS
- National Terrorism Advisory System
- DHS Seal
- DHS Headquarters
- Cybersecurity Efforts
- Secretaries of Homeland Security
- Images for kids
- See also
History of DHS
Why DHS Was Created
After the September 11 attacks, President George W. Bush wanted to improve how the U.S. protected itself. He created the Office of Homeland Security (OHS) in 2001. This office was meant to bring together different efforts to keep the country safe.
The goal of OHS was to:
The mission of the Office will be to develop and coordinate the implementation of a comprehensive national strategy to secure the United States from terrorist threats or attacks. The Office will coordinate the executive branch's efforts to detect, prepare for, prevent, protect against, respond to, and recover from terrorist attacks within the United States.
Later, on November 25, 2002, a law called the Homeland Security Act was passed. This law officially created the Department of Homeland Security. It brought together 22 different government agencies into one large department. This was a huge change, one of the biggest government reorganizations in many years.
Agencies That Joined DHS
When DHS was formed, many existing agencies moved under its umbrella. This helped to combine efforts for national security. Some of the important agencies that became part of DHS include:
- The U.S. Customs Service and Immigration and Naturalization Service (INS)
- The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), which helps with disasters
- The Transportation Security Administration (TSA), which handles airport security
- The United States Coast Guard, which protects waterways
- The United States Secret Service, known for protecting leaders and fighting financial crimes
This merger was a big step. It changed how the U.S. thought about protecting its people. The idea of "homeland security" became very important. It meant protecting the country not just from natural disasters, but also from threats like terrorism.

The Homeland Security Act of 2002 was signed into law by President Bush. This was the largest U.S. government change in 50 years. The first Secretary of Homeland Security was Tom Ridge. He started his job on January 24, 2003. Most of the agencies officially joined DHS by March 1, 2003.

Changes Over Time
After Tom Ridge, Michael Chertoff became the next Secretary in 2005. Under his leadership, DHS continued to grow and adapt. Later, Janet Napolitano became Secretary and introduced new security measures like full-body scanners.
More recently, in 2018, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) was created within DHS. CISA focuses on protecting important computer systems and physical structures across the U.S.
What DHS Does
The Department of Homeland Security works to protect the United States in many ways. While the Department of Defense handles military actions abroad, DHS focuses on safety within the country. Its main goal is to get ready for, prevent, and respond to emergencies, especially terrorism.
When DHS started, it took over the jobs of the U.S. Customs Service and the Immigration and Naturalization Service (INS). It then created new agencies to handle these tasks:
- U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) handles enforcing immigration and customs laws.
- United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) manages lawful immigration.
- U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) protects the borders, including the United States Border Patrol.
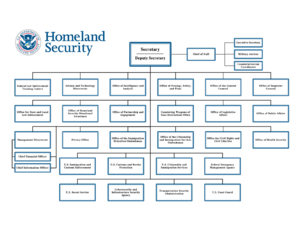
How DHS is Organized
The Department of Homeland Security is led by the United States Secretary of Homeland Security. The department has many different parts, each with its own specific job. These parts include agencies that carry out missions and others that support the whole department.
Key Agencies within DHS
Here are some of the main agencies that are part of DHS:
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services
This agency, known as USCIS, handles legal immigration to the United States. They process applications for citizenship, green cards, and other immigration benefits. Passports for U.S. citizens are handled by the United States Department of State, not DHS.
U.S. Coast Guard
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is a military branch that works on the water. They are responsible for maritime security, search and rescue missions, and enforcing laws at sea. In times of peace, they are part of DHS. During wartime, they can move under the United States Department of the Navy.
U.S. Customs and Border Protection
The U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) agency protects the U.S. borders. They stop illegal entry, fight crime, and make sure that legal trade and travel can happen smoothly. This includes the United States Border Patrol.
U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) is the main government group that works to protect the country's computer systems and important physical structures. They help manage and reduce risks to things like power grids and communication networks.
U.S. Federal Emergency Management Agency
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) helps the country prepare for and recover from disasters. This includes natural disasters like hurricanes, floods, and earthquakes. They work to protect people and property from all kinds of hazards.
U.S. Federal Law Enforcement Training Centers
The Federal Law Enforcement Training Centers (FLETC) provide training for law enforcement officers from many different agencies across the U.S. They help officers learn the skills they need to do their jobs safely and effectively.
U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement
U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) is responsible for enforcing federal laws related to border control, customs, immigration, and trade. They work to keep the country safe by investigating and stopping illegal activities.
U.S. Secret Service
The United States Secret Service (USSS) has two main jobs. First, they protect the President of the United States and other important government officials. Second, they work to stop financial crimes like counterfeiting money.
U.S. Transportation Security Administration
The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) protects U.S. transportation systems. This includes airport security, where they screen passengers and baggage. TSA was created after the September 11 attacks to make travel safer.
DHS Management Directorate
This part of DHS, called MGMT, handles the department's finances, human resources, and technology. They make sure DHS has the money, people, and tools it needs to do its job. They also oversee the U.S. Federal Protective Service, which protects federal buildings.
DHS Science and Technology Directorate
The S&T Directorate is the research and development arm of DHS. They work on new technologies and solutions to help protect the country. This includes research in areas like cybersecurity and ways to detect threats.
DHS Countering Weapons of Mass Destruction Office
The CWMD Office works to prevent chemical, biological, nuclear, and radiological attacks against the United States. They develop strategies and programs to protect the country from these very dangerous threats.
DHS Office of Intelligence and Analysis
The I&A Office is the intelligence part of DHS. They gather and share important information about threats with other parts of DHS and with state and local partners. This helps everyone stay informed and prepared.
DHS Office of Homeland Security Situational Awareness
The OSA provides a clear picture of what's happening across the country related to homeland security. They help coordinate operations and share information so that everyone involved knows the current situation.
DHS Office of Health Security
The OHS is the main health authority for DHS. They focus on the health and safety of DHS employees and also work on public health issues that relate to national security.
DHS Office of Inspector General
The OIG acts like a watchdog for DHS. They make sure that the department is working well, honestly, and responsibly. They conduct audits and investigations to ensure everything is done correctly.
DHS Office of the Secretary
This office supports the Secretary of Homeland Security. It includes various smaller offices that help manage the department's overall mission. These offices deal with things like civil rights, legal matters, and working with other government groups.
National Terrorism Advisory System
In 2011, DHS introduced the National Terrorism Advisory System (NTAS). This system replaced an older color-coded alert system. NTAS helps DHS share information about terrorist threats with the public and other security partners.
There are two types of advisories:
- Bulletins: These share important information about terrorism, even if there isn't a specific threat. They help people take general safety steps.
- Alerts: These are issued when there is specific and believable information about a terrorist threat.
* An Elevated Alert means there's credible information about an attack, but details like timing or target are general. * An Imminent Alert means the threat is very specific and expected to happen very soon.
DHS Seal
The official seal of the Department of Homeland Security has special meanings. It was designed to show the department's mission to protect Americans on land, at sea, and in the air.
The seal features a white American eagle in the center. The eagle's wings break through a circle, which suggests that DHS will work differently and break through old ways of doing things. The eagle holds an olive branch, which stands for peace, and arrows, which stand for protection.
On the eagle's chest is a shield with three parts. These parts represent the American homeland:
- The top part shows a dark blue sky with 22 stars. These stars stand for the 22 original agencies that came together to form DHS.
- The left part shows white mountains and a green plain, representing the land.
- The right part shows four waves, representing the oceans and seas.
DHS Headquarters


For many years, DHS had its temporary headquarters at the Nebraska Avenue Complex in Washington, D.C. This was a former naval facility.
In 2019, DHS headquarters staff began moving to a new, permanent location. This new headquarters is at the St. Elizabeths Hospital campus in Washington, D.C. This move was a big project aimed at bringing all of DHS's offices in the Washington area into one place.
Cybersecurity Efforts
DHS plays a key role in protecting the U.S. from cyberattacks. The National Cyber Security Division (NCSD) within DHS is responsible for managing cybersecurity risks. They also run US-CERT operations, which help respond to cyber incidents.
The DHS Science and Technology Directorate also helps with cybersecurity. They fund research to develop new ways to protect computer networks and information. This includes working on things like protecting the Internet's core systems and fighting identity theft.
In 2017, DHS officially said that state election systems are "critical infrastructure." This means they are very important to the country's safety. This step made it easier for states to get help from the federal government to protect their election systems from cyber threats.
Secretaries of Homeland Security
The Secretary of Homeland Security is the leader of the department. Here are the people who have served as Secretary:
- Tom Ridge (2003–2005)
- Michael Chertoff (2005–2009)
- Janet Napolitano (2009–2013)
- Jeh Charles Johnson (2013–2017)
- John F. Kelly (2017)
- Kirstjen M. Nielsen (2017–2019)
- Alejandro Mayorkas (2021–2025)
- Kristi Noem (2025–Now)
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Departamento de Seguridad Nacional de los Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Departamento de Seguridad Nacional de los Estados Unidos para niños