Herto Man facts for kids
 |
|
| Common name | Herto Man |
|---|---|
| Species | Homo sapiens idaltu |
| Age | 157±3 ka |
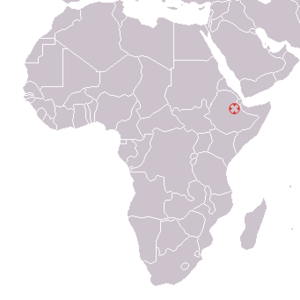
| Place discovered | Bouri Formation, Ethiopia |
| Date discovered | 1997 |
| Discovered by | Tim D. White and Berhane Asfaw |
Herto Man refers to ancient human remains found in 1997 in Ethiopia. These fossils are between 154,000 and 160,000 years old. The discovery was very important because it filled a large gap in the human fossil record. At the time, these were the oldest known Homo sapiens remains.
Scientists first described Herto Man as a new subspecies called "Homo sapiens idaltu." The word "Idaltu" means "elder" in the local Afar language. They thought Herto Man was a middle stage between older human forms and modern humans. However, many researchers today disagree with this classification. They argue that defining subspecies for ancient humans is tricky.
Herto Man made many stone tools. These tools show a mix of older and newer styles. They hunted and prepared animals like hippos and bovines near a lake. Some of the skulls found, including one from a child, have special marks. These marks suggest that Herto Man had unique ways of treating their dead.
Contents
Discovering Herto Man
What Was Found?
In 1997, fossils of Herto Man were found in Ethiopia. This area, called the Afar Triangle, is famous for ancient human discoveries. Scientists found several skull pieces and other bones. One important find was a nearly complete skull of an adult. Another was a skull from a child, about 6 or 7 years old. In total, remains from at least 12 individuals were uncovered.
Why Herto Man Was Important
In 2003, scientists used a special dating method to find the age of the Herto Man fossils. They were found to be between 154,000 and 160,000 years old. This was a big deal. At that time, there was a missing period in the human fossil record. This gap was between 300,000 and 100,000 years ago. Herto Man helped fill this gap. It gave clues about how early Homo sapiens evolved.
Before Herto Man, scientists already believed modern humans evolved in Africa. But they debated if this happened all over Africa or in one specific area. The age of Herto Man, and other similar fossils in East Africa, pointed to that region. Later, in 2017, even older H. sapiens fossils were found in Morocco. These were dated to 315,000 years ago. This showed that human evolution was happening across Africa. It also showed that our faces changed quickly, while our brains changed more slowly.
The Debate: Is It a New Subspecies?
When Herto Man was first described, scientists Tim D. White and Berhane Asfaw led the research. They believed Herto Man was almost, but not quite, like modern humans. They compared the Herto skull to other ancient skulls and modern ones. Because of its unique features, they gave it a new subspecies name: "H. s. idaltu." They saw it as a middle step in human evolution.
However, other scientists, like Chris Stringer, questioned this idea. They thought Herto Man looked similar to other early modern human fossils. Later studies in 2011 and 2014 also found that Herto Man was very similar to other early H. sapiens skulls. These studies suggested there wasn't enough reason to call it a separate subspecies.
The main problem is how scientists define "species" and "subspecies." It's hard to draw clear lines when studying a long, changing line of ancestors. Even the original discoverers still use the name "H. s. idaltu." But they agree that understanding how humans evolved is more important than the exact names.
How Herto Man Looked
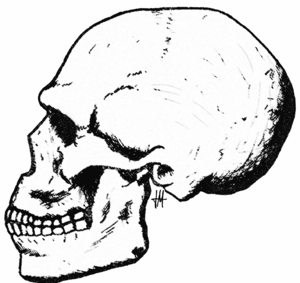
The Herto skull has features similar to modern humans. It has a high forehead and a rounded shape when viewed from the side. The face is also relatively flat. Its brain size was about 1,450 cubic centimeters. This is within the range of modern human brain sizes.
The skull is quite strong, with a noticeable brow ridge. The bones at the back and sides of the skull are also robust. These features are still seen in some modern humans. Compared to an average modern skull, the Herto skull is longer and larger overall. However, its cheekbones are not as strong.
Herto Man's Way of Life
Tools and Technology
The area where Herto Man lived was once a freshwater lake. Many stone tools were found there. These tools show a mix of techniques. Some were made using the Levallois technique, which is linked to the Middle Stone Age. Others were cleavers and bifaces, common in the older Acheulean period. This mix of tools is called "Transitional Acheulean." It shows that Herto Man used both old and new ways of making tools. This period of change lasted a long time.
Herto Man made sharp points and blades from obsidian. Other tools were made from basalt. They also made different kinds of scrapers. These tools helped them process food and other materials.
Hunting and Food
Evidence shows that Herto Man hunted large animals. They mainly butchered hippos, but also bovines (like cattle). Many animal bones found at the site have cut marks made by tools. This suggests a long tradition of hunting and preparing these animals. One spot even had many bones from both young and adult hippos.
Special Ways of Treating the Dead
Scientists found interesting marks on the Herto skulls. The adult skull (BOU-VP-16/1) had a small cut on its side. Another adult skull (BOU-VP-16/2) had many marks. These marks suggest that flesh was carefully removed from the skull. There was also evidence of scraping around the braincase. This might have been a symbolic act, not for eating. Parts of the skull's base were missing, suggesting it might have been placed as a skullcap.
The child's skull (BOU-VP-16/5) also had deep cut marks. These marks were on the underside of the skull bones. The base of this skull was broken, and its edges were smoothed. This is similar to how some modern tribes treat the bones of their dead. These findings suggest that Herto Man had special rituals for their deceased.
See also
 In Spanish: Homo sapiens idaltu para niños
In Spanish: Homo sapiens idaltu para niños
- Blombos Cave
- Florisbad Skull
- Mumba Cave
- Omo remains
- List of fossil sites
- List of human evolution fossils